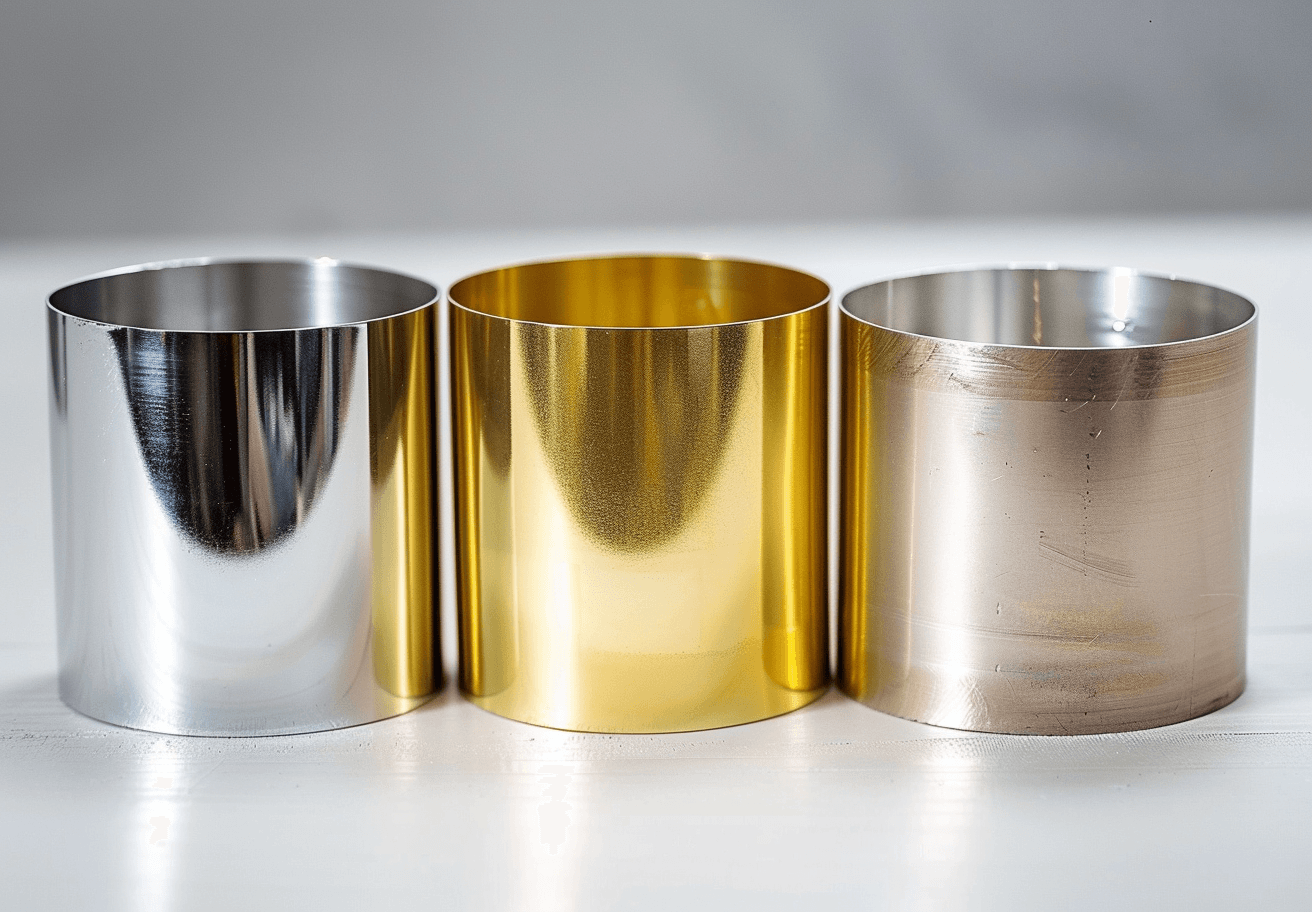
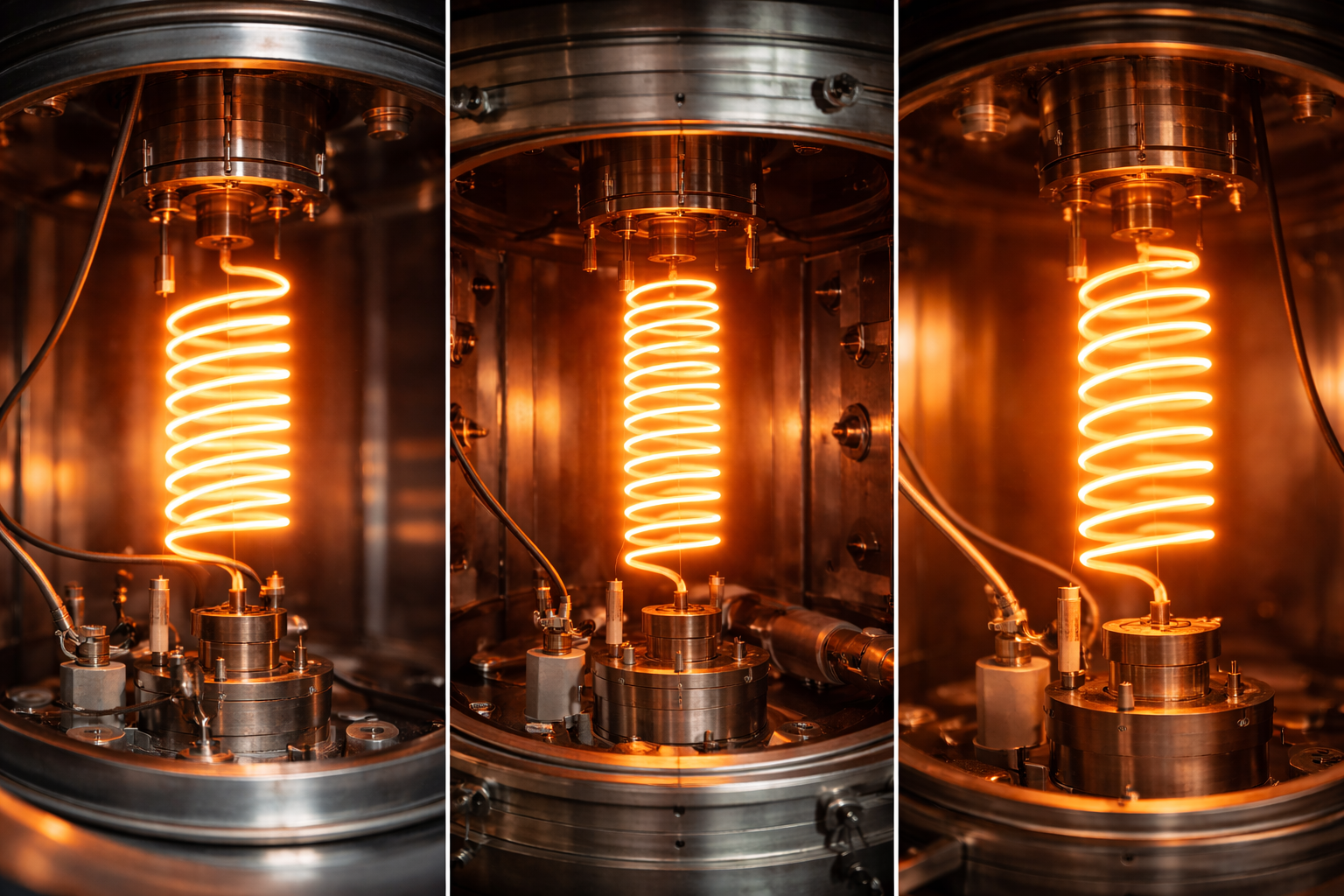
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a widely utilized thin-film deposition process in various industries. In essence, PVD coating is a method by which a solid material is vaporized and deposited onto a substrate to form a thin, durable layer. The process involves placing the material in a vacuum chamber, where it is vaporized and allowed to condense onto the surface of the target object, forming a thin, protective film. The PVD technique is essential in enhancing the properties of substrates such as metals, ceramics, and polymers, offering superior performance, longevity, and aesthetic appeal.
PVD coatings have gained significant popularity due to their range of advantages over traditional coating techniques. These coatings are harder, more wear-resistant, and exhibit enhanced corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications. Additionally, PVD coatings can alter the appearance of products, offering the option to change their color or finish to meet specific design requirements.
The PVD Coating Process
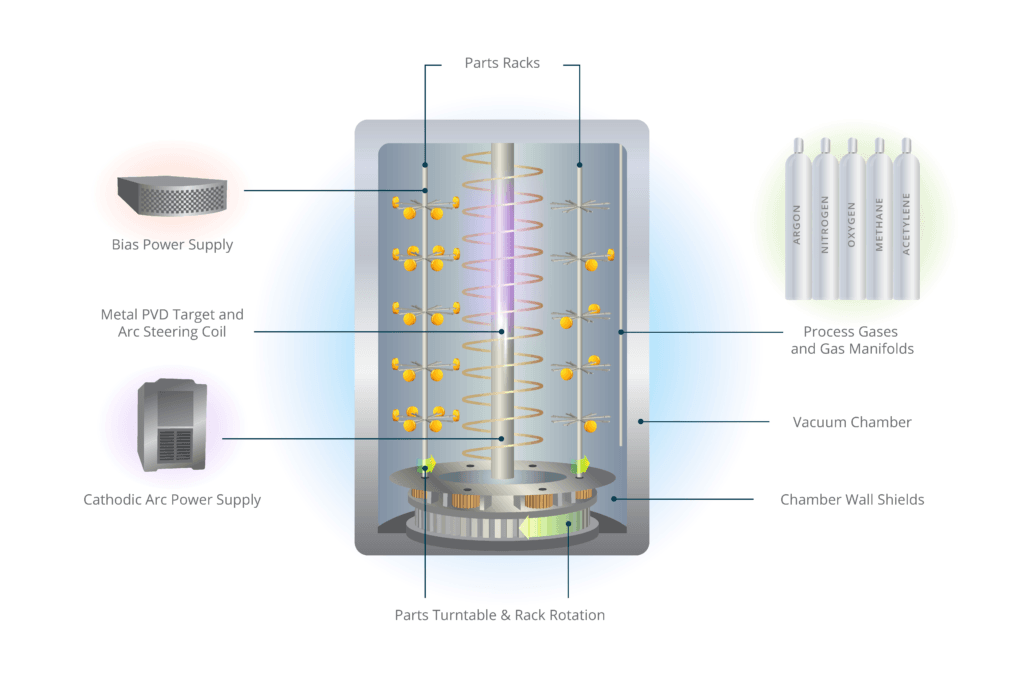
The PVD coating process involves several key steps to ensure that the final thin film is of high quality and durability. While there are variations in the exact procedure depending on the type of PVD process used, the following general steps outline the typical process:
- Material Selection and Preparation: The process begins with the selection of the material to be coated, such as a metal, ceramic, or plastic substrate. The material to be vaporized, also known as the target material, is placed in a vacuum chamber.
- Vacuum Creation: The chamber is evacuated to create a high-vacuum environment. This is critical to preventing contamination during the deposition process.
- Vaporization: The target material is heated or bombarded with electrons, ions, or photons, which cause it to vaporize. This vaporized material then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the surface of the substrate.
- Deposition: The vaporized material condenses on the substrate to form a thin film. Depending on the PVD technique used, the material may form a uniform coating or a more complex structure.
- Purging the Chamber: Once the coating has been applied, the chamber is purged with an inert gas to remove any residual vapors, ensuring the coating adheres properly and is free from contaminants.
Types of PVD Coating Methods
PVD coatings can be applied using several different methods, each offering unique advantages and applications. These include:
Thermal Evaporation
In thermal evaporation, the target material is heated until it vaporizes. The vapor then condenses on the substrate, forming a thin, uniform coating. This method is commonly used for metals and is relatively simple and cost-effective.
Sputter Deposition
Sputtering involves bombarding a target material with energetic ions, causing atoms or molecules from the target to be ejected and deposited onto the substrate. This technique can be used with a wide variety of materials and allows for precise control over the film’s properties.
Ion Plating
Ion plating is a more advanced PVD technique that uses ions instead of electrons to bombard the target material. This process, sometimes referred to as Ion Beam-Assisted Deposition (IBAD), enables the deposition of coatings at lower temperatures and higher rates, making it suitable for sensitive materials.
Are PVD Coatings Safe?
When it comes to safety, PVD coatings are generally considered safe once the process is complete. The particles involved in the PVD process are small, and although they may be hazardous if inhaled during application, they are securely bonded to the substrate after deposition. For this reason, safety measures should be in place during the application phase to prevent exposure. Once the coating has been applied, it is safe to handle, and no harmful particles are released into the air. Always ensure that the PVD process is conducted in a controlled, well-ventilated environment.
Advantages of PVD Coatings
PVD coatings offer numerous benefits that make them a superior choice for many industries:
- Superior Resistance to Corrosion and Scratching: PVD coatings provide exceptional resistance to wear, scratching, and corrosion. This is due to the strong bond formed between the coating and substrate in a vacuum environment, which eliminates contamination and ensures a durable layer.
- Increased Durability: PVD coatings enhance the durability of substrates by making them more resistant to oxidation and other forms of degradation. The vacuum application environment eliminates the presence of moisture and oxygen, which would otherwise cause corrosion or wear over time.
- Wide Range of Material Compatibility: PVD coatings can be applied to a variety of substrates, including metals, ceramics, glass, and plastics. This flexibility allows manufacturers to coat a wide range of products without worrying about material compatibility.
- Aesthetic Improvements: PVD coatings can alter the appearance of a product, providing a shiny, reflective surface or changing the color of the material. This makes PVD coatings highly sought after in industries where aesthetics play an important role, such as the automotive, watch, and fashion industries.
Applications of PVD Coatings
PVD coatings are utilized across numerous industries where enhanced material properties such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics are essential. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Cutting Tools
PVD coatings are widely used on cutting tools such as drills, milling cutters, and lathes. The hardness and wear resistance of PVD coatings extend the life of these tools, reducing the need for frequent replacements and improving machining efficiency.
2. Automotive Components
In the automotive industry, PVD coatings are applied to engine parts, such as pistons, valvetrain components, and other high-performance parts. These coatings help improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and overall component longevity.
3. Optical Lenses
PVD coatings are frequently used to enhance the performance of optical lenses. These coatings improve light transmission, reduce glare, and increase durability, making them essential for high-quality lenses used in cameras, eyeglasses, and other optical devices.
4. Medical Implants
PVD coatings are often applied to medical implants, such as orthopedic devices and dental implants. These coatings improve the biocompatibility of the implants and help prevent corrosion, ensuring long-term durability inside the human body.
5. Watch Components
The watch industry is another area where PVD coatings are used extensively. These coatings not only provide enhanced durability but also allow for the creation of aesthetically pleasing finishes, such as gold, black, or other custom colors, improving the visual appeal of watches.
6. Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense industries, PVD coatings are used on components like turbine blades, landing gear, and other parts exposed to harsh environments. The coatings protect these components from wear, heat, and corrosion, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
Suppliers of PVD Coating Services
When seeking PVD coating services, it is essential to partner with a reliable and experienced supplier. Many suppliers offer a wide range of coating materials and types to meet the specific needs of various industries. TFM, a leading provider of thin-film materials and coating services, offers high-quality PVD coatings for a range of applications, ensuring excellent performance and durability.
When choosing a supplier for PVD coatings, consider the following factors:
- Material Variety: Ensure the supplier offers a broad selection of materials for PVD coatings, including metals, ceramics, and polymers.
- Customization: The ability to customize the coating to meet specific requirements, including color, thickness, and finish, is crucial for industries such as fashion and automotive.
- Quality Control: Select a supplier that emphasizes strict quality control and ensures that all coatings are free from defects, ensuring the final product meets industry standards.
- Technical Expertise: A supplier with technical expertise in PVD coating technology can offer valuable insights and help select the best process for your specific needs.
- Customer Support: Look for a supplier that provides excellent customer support, helping you navigate the coating process and ensuring a smooth partnership.
Conclusion
PVD coatings are transforming industries by providing enhanced material properties such as superior resistance to wear, corrosion, and scratching. With applications ranging from cutting tools to medical implants, these coatings are crucial for industries seeking to improve the durability, performance, and aesthetics of their products. Working with a trusted supplier like TFM ensures access to high-quality PVD coating services and expertise that can help meet your specific coating needs.
The PVD process is an effective solution for manufacturers looking to extend the lifespan of components, improve performance, and add aesthetic appeal. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, medical, or fashion industry, PVD coatings offer a wide range of benefits that can give your products a competitive edge.