Introduction
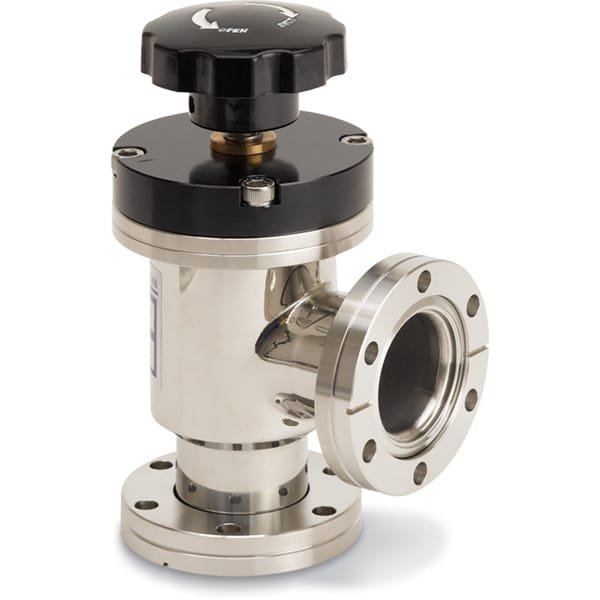
An angle valve is a specialized type of valve that is commonly used in plumbing, industrial, and HVAC systems to control the flow of fluids or gases. Unlike traditional straight valves, which maintain a direct line of flow, angle valves are designed with the inlet and outlet positioned at a 90-degree angle to each other. This unique configuration allows them to be used in situations where space is limited, or where pipes must change direction. The primary function of an angle valve is to regulate the flow of substances within a system, and its design makes it particularly useful for controlling the flow in tighter or more complex piping layouts.
Angle valves are typically used in systems where the piping needs to turn or where space constraints require a more compact solution. They allow for the easy redirection of flow without the need for extensive alterations to the overall piping structure. Their ability to regulate flow effectively, even in confined spaces, makes them an essential component in many industries, including residential plumbing, commercial heating and cooling, and industrial fluid handling systems.
The key components of an angle valve include the valve body, which houses the internal mechanisms, a handle or actuator used to control the valve, and the inlet and outlet ports that control fluid or gas flow. These valves can be operated manually or automatically, depending on the needs of the system. The handle or actuator allows users to open, close, or adjust the valve to control the flow of fluids or gases to specific levels.
Angle valves are available in various materials, including brass, stainless steel, and plastic, each selected for the particular demands of the application. Brass and stainless steel are often used in industrial applications due to their strength and durability, while plastic versions are more common in household plumbing systems for ease of installation and cost-effectiveness.
Applications of Angle Valves
Angle valves are versatile components that can be found in a wide array of applications, from household plumbing to industrial systems. One of the most common uses is in residential plumbing, where they are installed in places where pipes must turn, such as under sinks or behind toilets. Their ability to redirect the flow of water at a 90-degree angle helps keep the plumbing system efficient, even in confined spaces.
In commercial and industrial heating and cooling systems, angle valves help manage the flow of fluids such as water, steam, or refrigerants. In such systems, precise control of fluid flow is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance. Angle valves are used to regulate the flow of these fluids to radiators, air handling units, and other parts of the heating or cooling system.
In industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and manufacturing, angle valves play a critical role in the control of fluids and gases. These systems often require precise control over the flow, pressure, and direction of substances within their pipelines. Angle valves help achieve this control by offering a compact and efficient solution for systems where pipes need to change direction or where space constraints limit the installation of traditional straight valves.
Angle valves are also used in medical equipment, particularly in systems that require the precise control of fluids, such as intravenous (IV) fluid delivery systems or oxygen regulators. In these applications, the reliability and accuracy of the valve are paramount to ensure the proper delivery of critical fluids to patients.
In hydraulic and pneumatic systems, angle valves are employed to regulate the direction and flow of fluids under pressure. These systems often operate under high-pressure conditions, making it essential to maintain precise control over the flow of the fluid. Angle valves help manage the pressure and flow rate of fluids in such systems, ensuring that they operate safely and efficiently.
Benefits of Using Angle Valves
Angle valves offer several significant advantages, particularly in applications where space is a premium or where piping layouts require complex configurations. One of the key benefits is their compact design, which allows them to be installed in tight spaces where a traditional straight valve would be difficult or impossible to use. By positioning the inlet and outlet at a 90-degree angle, angle valves can be integrated into systems where space limitations would otherwise hinder the installation of larger, more cumbersome valves.
Another significant advantage of angle valves is their ability to provide precise control over the flow of fluids or gases. The internal mechanism of an angle valve can be adjusted to control the flow rate or shut off the flow entirely, providing more accurate regulation compared to other types of valves. This level of control is essential in many applications, such as heating and cooling systems, where maintaining consistent flow rates is crucial for system efficiency.
Angle valves are also known for their durability and versatility. Depending on the material used for construction, these valves can withstand harsh environmental conditions, high pressures, and extreme temperatures. For instance, stainless steel angle valves are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in chemical processing and other industrial applications where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Due to their simple design and easy operation, angle valves are also cost-effective compared to other types of valves. They offer an efficient and affordable solution for applications where space, flow control, and durability are important considerations. In many cases, the cost savings from using an angle valve, as opposed to more complex valve types, can make a significant difference in the overall cost of the system.
What is the Difference Between Straight and Angled Valves?
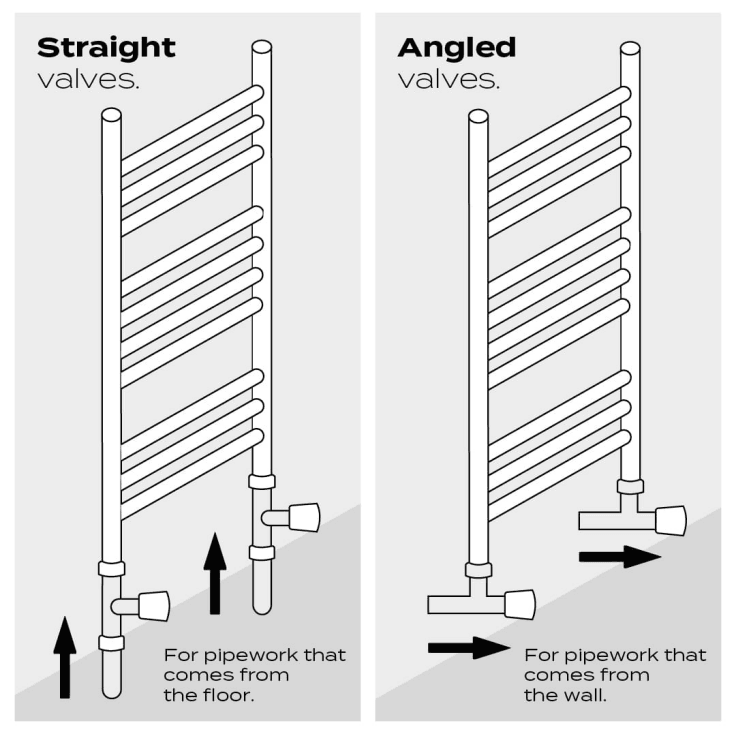
Straight valves and angle valves are both designed to control the flow of fluids or gases within a system, but they differ significantly in their design, functionality, and typical applications. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the right type of valve for a particular use case.
Straight valves, as the name suggests, have both the inlet and outlet aligned along a straight path. This straightforward design makes straight valves ideal for systems where the flow of fluid or gas follows a direct, uninterrupted route. The simplicity of a straight valve’s design means that it is often easier to install and requires less space compared to more complex valve configurations. Straight valves are commonly used in systems where the piping runs in a linear fashion, such as in water distribution networks or oil pipelines.
In contrast, angle valves are designed with the inlet and outlet positioned at a 90-degree angle to each other. This angled design allows for greater flexibility in how the valve can be installed, particularly in systems where the piping must change direction. Angle valves are especially useful in situations where space constraints or tight piping layouts make a straight valve impractical. By redirecting the flow of fluid or gas, angle valves provide a more versatile solution for controlling flow in complex piping systems.
In terms of functionality, both straight and angle valves are used to regulate the flow of substances, but the mechanism by which they do so can differ. Straight valves typically operate through a linear motion, where the valve either opens or closes to allow or restrict the flow. Angle valves, on the other hand, are designed to manage flow at an angle, often with a more sophisticated mechanism that can handle changes in direction or pressure within the system.
When it comes to installation, straight valves are generally easier to install due to their simpler design. They can be easily integrated into systems with direct, linear pipelines. Angle valves, however, require more careful planning during installation. Their ability to redirect flow means that they are better suited for complex systems, where the layout involves turns or changes in direction. While angle valves may require additional effort to install, their ability to function in tight spaces and redirect flow makes them invaluable in many applications.
Another key difference between straight and angle valves is their application suitability. Straight valves are best suited for systems with simple, direct piping, where the flow follows a straight line. These valves are commonly used in residential plumbing, water distribution, and other applications where space is not a limiting factor. Angle valves, on the other hand, are often used in situations where space is limited or where the piping must change direction, such as in industrial systems, heating and cooling systems, and medical equipment.
The performance of both types of valves is generally reliable, but angle valves offer a distinct advantage in certain applications. For instance, in systems where precise control over fluid flow is required, or where space constraints make a straight valve impractical, angle valves provide the flexibility and efficiency needed to maintain optimal system performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both straight and angle valves serve the fundamental purpose of regulating the flow of fluids or gases, they differ significantly in their design, functionality, and application. Straight valves are best suited for systems with simple, direct piping, where the flow follows a linear path. They are easy to install and provide efficient flow control in straightforward applications.
Angle valves, however, offer greater flexibility, particularly in complex systems where space is constrained, or where the flow must change direction. Their 90-degree angle design makes them ideal for applications such as heating systems, industrial piping, and medical equipment, where space-saving and flow control are essential. By understanding the unique characteristics of both types of valves, engineers and technicians can make informed decisions about which valve is best suited for their specific application.



