Aluminum Scandium Sputtering Target (Al-Sc)
Introduction
Aluminum Scandium (Al-Sc) Sputtering Targets are advanced materials widely used in thin film deposition, especially in the production of high-performance semiconductors, optoelectronics, and display technologies. By combining aluminum’s excellent conductivity with scandium’s unique structural benefits, Al-Sc alloys provide superior thin film characteristics compared to pure aluminum targets.
Detailed Description
The Aluminum Scandium Sputtering Target is typically prepared by alloying aluminum with a small percentage of scandium. Even trace additions of scandium significantly improve film adhesion, grain refinement, and thermal stability. This alloy system enhances the electronic properties of deposited films, enabling higher efficiency and durability.
Purity: Available up to 99.9% depending on application needs
Composition: Custom scandium doping levels (commonly 1–5 at%)
Shapes: Circular, rectangular, and custom dimensions
Bonding Options: Indium, elastomer, or copper backing for better thermal management
The targets are manufactured using vacuum melting, powder metallurgy, or hot-press sintering to ensure uniform composition and consistent sputtering performance.
Applications
Al-Sc sputtering targets are widely adopted in:
Semiconductor industry – thin films for integrated circuits
Display manufacturing – OLED, LCD, and next-generation displays
Optoelectronics – sensors and laser components
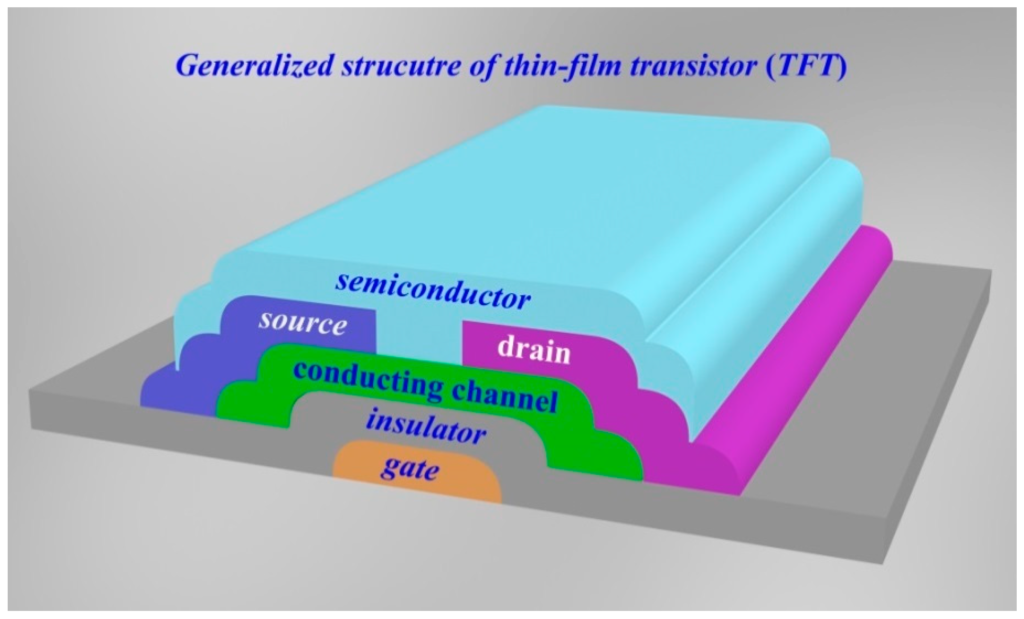
Thin film transistors (TFTs) – enhanced channel and gate performance
Energy applications – photovoltaic devices and advanced coatings
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% (3N) | Ensures low contamination |
| Composition | 1–5 at% Sc in Al (customizable) | Enhances electrical & mechanical performance |
| Diameter | 25 – 300 mm (custom sizes) | Matches system requirements |
| Thickness | 3 – 6 mm | Controls sputtering rate |
| Bonding | Indium, Elastomer, Copper backing | Improves heat transfer and stability |
| Process Method | Powder metallurgy / Vacuum casting | Ensures uniform microstructure |
Comparison with Related Materials
| Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Scandium (Al-Sc) | Improved adhesion & grain refinement | Semiconductors, TFTs |
| Pure Aluminum (Al) | Cost-effective, conductive | General coatings |
| Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) Alloy | High wear resistance | Power electronics |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can scandium content be customized? | Yes, we offer different scandium doping levels based on customer needs. |
| What is the delivery time? | Normally 2–3 weeks, depending on size and order quantity. |
| How are the targets packaged? | Vacuum-sealed with protective foam in export-safe cartons or crates. |
| What industries use Al-Sc targets most? | Semiconductor, display, optoelectronics, and photovoltaic industries. |
Conclusion
Aluminum Scandium Sputtering Targets combine the conductivity of aluminum with the structural advantages of scandium, making them ideal for high-performance thin films. With customizable compositions, strict purity control, and various bonding options, these targets are well-suited for cutting-edge research and industrial production.
For detailed specifications and a quotation, please contact us at sales@thinfilmmaterials.com.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.