Introduction
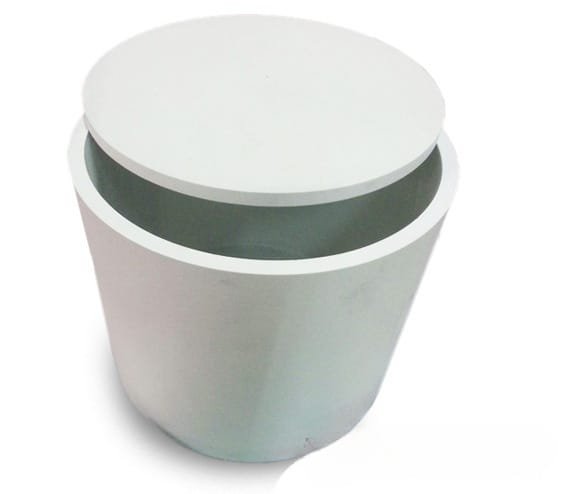
BN1662 Boron Nitride Crucibles are high-performance ceramic crucibles engineered for high-temperature, high-purity processing where chemical inertness and thermal stability are critical. Thanks to the unique properties of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), these crucibles are widely used in vacuum, inert-gas, and reactive atmospheres for melting, evaporation, and crystal growth applications in research and advanced manufacturing.
Detailed Description
The BN1662 Boron Nitride Crucible is typically manufactured from high-purity hexagonal boron nitride using hot-pressing or advanced sintering techniques. This process produces a dense, fine-grained microstructure that delivers excellent thermal shock resistance, low wettability to most molten metals, and outstanding chemical inertness.
One of the key advantages of BN crucibles is their non-wetting behavior toward many molten metals and alloys, including aluminum, gallium, indium, and various rare-earth metals. This property minimizes contamination and makes material removal easy after processing. In addition, boron nitride maintains excellent electrical insulation while offering good thermal conductivity, allowing precise temperature control during heating cycles.
Compared with oxide ceramics such as alumina, BN crucibles exhibit superior resistance to thermal cracking and do not react readily with molten metals at elevated temperatures. These characteristics make BN1662 crucibles especially suitable for high-purity evaporation sources, compound synthesis, and laboratory-scale production where material integrity is paramount.
Applications
BN1662 Boron Nitride Crucibles are commonly used in:
Vacuum and inert-atmosphere melting
Metal and alloy evaporation processes
Semiconductor and electronic material research
Crystal growth and solidification studies
Rare-earth and reactive metal processing
High-temperature laboratory experiments
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) | Ensures chemical inertness and purity |
| Purity | ≥ 99% BN | Minimizes contamination |
| Manufacturing Method | Hot-pressed / sintered | Provides uniform density and strength |
| Maximum Working Temperature | ~1800 °C (in inert atmosphere) | Supports high-temperature applications |
| Electrical Properties | Excellent insulation | Suitable for electronic processing |
| Wettability | Non-wetting to most metals | Enables clean melting and easy release |
Comparison with Related Crucible Materials
| Crucible Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Boron Nitride (BN) | Non-wetting, thermal shock resistant | High-purity metal processing |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | High hardness, cost-effective | General ceramic melting |
| Graphite | Excellent thermal conductivity | Non-oxidizing environments |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What makes BN crucibles different from alumina crucibles? | BN crucibles offer better thermal shock resistance and non-wetting behavior. |
| Can BN1662 crucibles be used in vacuum? | Yes, they are well suited for vacuum and inert atmospheres. |
| Are custom sizes available? | Yes, dimensions and wall thickness can be customized. |
| Do BN crucibles react with molten metals? | BN is highly inert and resists reaction with most molten metals. |
| How should BN crucibles be handled? | Handle carefully to avoid mechanical shock; store in clean, dry packaging. |
Available Shapes and Customization
TFM provides a range of custom shapes and dimensions for boron nitride crucibles. The available shapes are described by the following parameters:
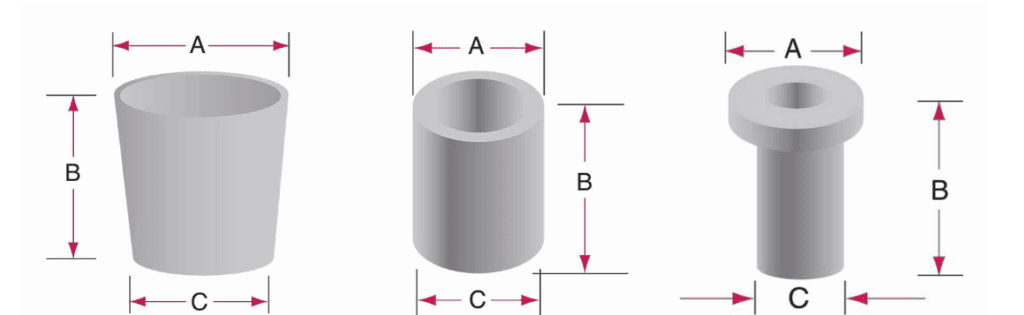
- A: Top Diameter
- B: Height
- C: Bottom Diameter
For customized solutions, please reach out to us with your specific requirements.
Packaging
Our BN1662 Boron Nitride Crucibles are individually cleaned and securely packaged with protective cushioning to prevent chipping or contamination. Each crucible is clearly labeled to ensure traceability and safe handling during storage and transportation.
Conclusion
BN1662 Boron Nitride Crucibles provide a reliable and high-purity solution for demanding high-temperature and vacuum applications. With excellent thermal stability, chemical inertness, and non-wetting behavior, BN crucibles are an ideal choice for advanced research, evaporation processes, and reactive metal handling.
For detailed specifications and a quotation, please contact us at sales@thinfilmmaterials.com.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.