Covered Boat Sources
Overview
Covered Boats Wrapped Covered
Covered Boats

#288W: Tungsten, 2.6 Volt, 400 Amps, 1040 Watts, 1800°C
#289TA: Tantalum, 1.44 Volt, 296 Amps, 427 Watts, 1600°C
#290W: Tungsten, 1.50 Volt, 444 Amps, 666 Watts, 1800°C
Covered Boats with Hole
Covered Boats
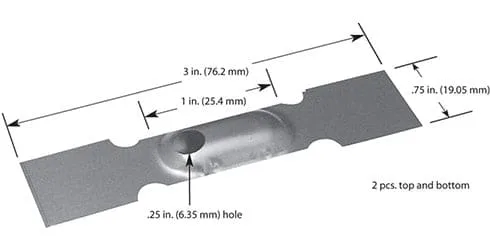
#292MO: Molybdenum, 0.88 Volt, 301 Amps, 265 Watts, 1400°C
#293TA: Tantalum, 1.68 Volt, 295 Amps, 496 Watts, 1600°C
#294W: Tungsten, 1.50 Volt, 375 Amps, 562 Watts, 1800°C
Covered Boats
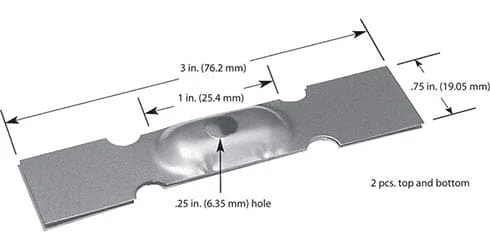
#295MO: Molybdenum, 1.24 Volt, 202 Amps, 250 Watts, 1400°C
#296TA: Tantalum, 2.28 Volt, 190 Amps, 433 Watts, 1600°C
#297W: Tungsten, 2.21 Volt, 256 Amps, 566 Watts, 1800°C
#298MO: Molybdenum, 0.83 Volt, 297 Amps, 247 Watts, 1400°C
#299TA: Tantalum, 1.77 Volt, 329 Amps, 582 Watts, 1600°C
#300W: Tungsten, 1.70 Volt, 386 Amps, 656 Watts, 1800°C
Covered Boats
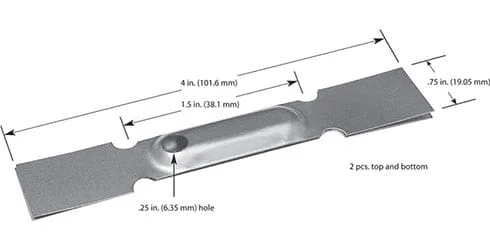
#301MO: Molybdenum, 1.14 Volt, 300 Amps, 342 Watts, 1400°C
#302TA: Tantalum, 2.16 Volt, 272 Amps, 588 Watts, 1600°C
#303W: Tungsten, 2.30 Volt, 375 Amps, 862 Watts, 1800°C
Covered Boats
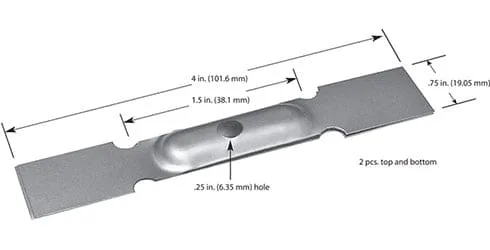
#304MO: Molybdenum, 1.10 Volt, 278 Amps, 306 Watts, 1400°C
#305TA: Tantalum, 2.40 Volt, 293 Amps, 703 Watts, 1600°C
#306W: Tungsten, 2.14 Volt, 383 Amps, 820 Watts, 1800°C
Covered Boat Baffle Inserts
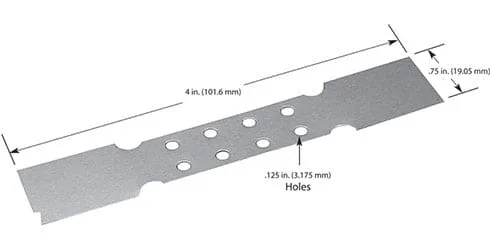
#307MO: Molybdenum, 1.46 Volt, 94 Amps, 137 Watts, 1400°C
#308TA: Tantalum, 3.27 Volt, 94 Amps, 307 Watts, 1600°C
#309W: Tungsten, 3.26 Volt, 144 Amps, 469 Watts, 1800°C
Frequently Asked Questions
What are boat sources in thermal evaporation?
Boat sources are typically made from high-purity tungsten, tantalum, or molybdenum due to their high melting points, low vapor pressures, and durability under high thermal loads. In some cases, an alumina coating is applied to prevent wetting or alloying with the evaporant.
What materials are commonly used to fabricate boat sources?
Metal powders are widely used in industries such as automotive (for brake pads and engine components), aerospace, electronics, batteries, capacitors, magnetic materials, and tooling.
How do boat sources differ from crucibles in evaporation systems?
Unlike crucibles that often use a separate heater and may provide larger volumes for thick films, boat sources integrate the heating element with the evaporant container. Boats are especially suitable for upward evaporation and offer faster heating and more controlled deposition for thinner films.
What factors should be considered when selecting a boat source?
Key considerations include the type of evaporant material, boat material compatibility, required evaporation rate, power supply (voltage and current demands), boat geometry (such as dimpled or trough designs), and whether corrosion or wetting issues need to be minimized via coatings.
What advantages do alumina-coated boat sources offer?
Alumina coatings on boat sources help prevent the molten evaporant from “wetting” the entire source, which can lead to non-uniform deposition and early failure. The inert alumina layer minimizes chemical reactions and migration of the material, leading to improved film uniformity and extended boat life.
How is the evaporation rate controlled using boat sources?
The evaporation rate is primarily controlled by adjusting the electrical current supplied to the boat. The increased current raises the boat’s temperature, which in turn increases the vapor pressure of the evaporant. Fine tuning the current allows precise control over the film thickness and deposition rate.
What challenges are associated with boat source evaporation?
Common challenges include material wetting or creeping (which can lead to contamination and loss of material), alloying between the evaporant and boat material (especially for reactive metals), and the need for high power input. Proper design and coating strategies are critical to mitigate these issues.
How do boat source designs vary?
Boat sources come in various designs—such as dimpled, trough, or flat configurations—to optimize the hot zone where the material melts. Some designs include isolated hot zones or directional features to control evaporation patterns and improve film uniformity.
Can boat sources be used for a wide range of materials?
Yes. Boat sources are versatile and can be used to evaporate many metals, alloys, and even some compound materials. However, material-specific considerations (e.g., reactivity and melting point) may require selecting a particular boat material or applying an alumina coating to ensure successful deposition.
What maintenance practices ensure the longevity of a boat source?
To extend the life of a boat source, it’s important to operate within its specified power range, avoid overfilling with evaporant, and use proper cooling periods between runs. Regular inspection for signs of wear or contamination and replacing boats when necessary are also key practices.
How do boat sources impact the uniformity of the deposited film?
The geometry of the boat (e.g., whether it’s dimpled or has a trough design) influences the distribution of heat and the vapor flux. A well-designed boat source provides a concentrated hot zone that promotes a uniform evaporation rate, leading to more even thin film deposition on the substrate.
What troubleshooting steps can be taken if a boat source fails prematurely?
If a boat source fails, check for issues such as excessive wetting or alloying of the evaporant with the boat material, incorrect power settings, or overfilling. Adjusting the current, using an alumina-coated boat, or selecting an alternative material may resolve the problem.

