Dimple Boat Sources
Overview
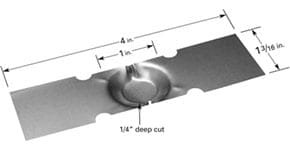
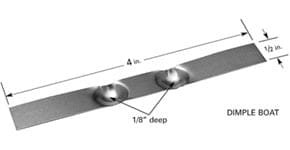
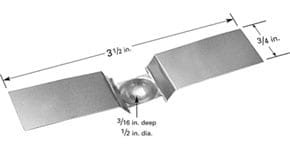
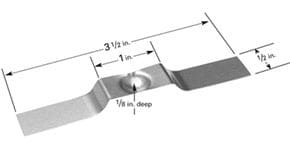
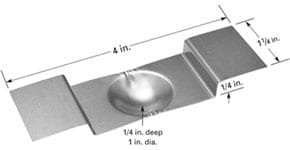
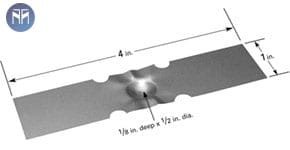
Dimple boats available in various materials and lengths. Dimple area allows for material to be placed in one area, allowing for more focused evaporation area. Be sure to review power requirements when selecting source.
Please Select a Category:
Dimple Boats
Dimple Boats

#307MO: Molybdenum, 1.21 Volt, 108 Amps, 131 Watts, 1400°C
#308TA: Tantalum, 2.48 Volt, 138 Amps, 342 Watts, 1600°C
#309W: Tungsten, 2.49 Volt, 181 Amps, 451 Watts, 1800°C
#310MO: Molybdenum, 0.96 Volt, 180 Amps, 173 Watts, 1400°C
#311TA: Tantalum, 1.80 Volt, 155 Amps, 279 Watts, 1600°C
#312W: Tungsten, 1.92 Volt, 258 Amps, 495 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#313MO: Molybdenum, 1.70 Volt, 87 Amps, 148 Watts, 1400°C
#314TA: Tantalum, 3.80 Volt, 93 Amps, 353 Watts, 1600°C
#315W: Tungsten, 3.95 Volt, 185 Amps, 731 Watts, 1800°C
#316MO: Molybdenum, 1.25 Volt, 121 Amps, 151 Watts, 1400°C
#317TA: Tantalum, 2.69 Volt, 135 Amps, 363 Watts, 1600°C
#318W: Tungsten, 2.84 Volt, 194 Amps, 551 Watts, 1800°C
#319W: Tungsten, 2.29 Volt, 253 Amps, 579 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#320MO: Molybdenum, 2.01 Volt, 132 Amps, 265 Watts, 1400°C
#321TA: Tantalum, 4.43 Volt, 146 Amps, 647 Watts, 1600°C
#322W: Tungsten, 3.50 Volt, 280 Amps, 980 Watts, 1800°C
#323MO: Molybdenum, 1.30 Volt, 186 Amps, 242 Watts, 1400°C
#324TA: Tantalum, 2.98 Volt, 207 Amps, 617 Watts, 1600°C
#325W: Tungsten, 3.10 Volt, 325 Amps, 1008 Watts, 1800°C
#326W: Tungsten, 2.76 Volt, 386 Amps, 1065 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#327MO: Molybdenum, 1.36 Volt, 257 Amps, 350 Watts, 1400°C
#328TA: Tantalum, 3.27 Volt, 281 Amps, 919 Watts, 1600°C
#329W: Tungsten, 3.08 Volt, 407 Amps, 1254 Watts, 1800°C
#330MO: Molybdenum, 1.09 Volt, 315 Amps, 343 Watts, 1400°C
#331TA: Tantalum, 2.31 Volt, 333 Amps, 769 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats

#332MO: Molybdenum, 1.34 Volt, 260 Amps, 348 Watts, 1400°C
#333TA: Tantalum, 2.89 Volt, 262 Amps, 757 Watts, 1600°C
#334W: Tungsten, 3.06 Volt, 411 Amps, 1258 Watts, 1800°C
#335MO: Molybdenum, 1.12 Volt, 318 Amps, 356 Watts, 1400°C
#336TA: Tantalum, 2.35 Volt, 333 Amps, 783 Watts, 1600°C
#337TA: Tantalum, 1.86 Volt, 431 Amps, 802 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats

#338MO: Molybdenum, 1.36 Volt, 316 Amps, 430 Watts, 1400°C
#339TA: Tantalum, 2.97 Volt, 340 Amps, 1010 Watts, 1600°C
#340W: Tungsten, 3.21 Volt, 525 Amps, 1685 Watts, 1800°C
#341MO: Molybdenum, 1.12 Volt, 417 Amps, 467 Watts, 1400°C
#342TA: Tantalum, 2.00 Volt, 366 Amps, 732 Watts, 1600°C
#343TA: Tantalum, 1.93 Volt, 539 Amps, 1040 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats

#344MO: Molybdenum, 1.61 Volt, 559 Amps, 900 Watts, 1400°C
#345TA: Tantalum, 3.12 Volt, 601 Amps, 1875 Watts, 1600°C
#346W: Tungsten, 3.31 Volt, 811 Amps, 2684 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Deep Cut
Dimple Boats

#347MO: Molybdenum, 2.10 Volt, 198 Amps, 416 Watts, 1400°C
#348TA: Tantalum, 4.50 Volt, 221 Amps, 994 Watts, 1600°C
#349W: Tungsten, 4.29 Volt, 316 Amps, 1356 Watts, 1800°C
#350MO: Molybdenum, 1.43 Volt, 281 Amps, 402 Watts, 1400°C
#351TA: Tantalum, 3.36 Volt, 322 Amps, 1082 Watts, 1600°C
#352W: Tungsten, 3.30 Volt, 451 Amps, 1488 Watts, 1800°C
#353TA: Tantalum, 2.56 Volt, 406 Amps, 1039 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats Double Dimple
Dimple Boats

#354MO: Molybdenum, 1.92 Volt, 86 Amps, 165 Watts, 1400°C
#355TA: Tantalum, 3.74 Volt, 92 Amps, 344 Watts, 1600°C
#356W: Tungsten, 3.81 Volt, 131 Amps, 499 Watts, 1800°C
#357MO: Molybdenum, 1.27 Volt, 127 Amps, 161 Watts, 1400°C
#358TA: Tantalum, 2.69 Volt, 132 Amps, 355 Watts, 1600°C
#359W: Tungsten, 2.93 Volt, 187 Amps, 548 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Inverted Top Hat Deep Well
Dimple Boats

#360MO: Molybdenum, 1.84 Volt, 201 Amps, 370 Watts, 1400°C
#361TA: Tantalum, 4.26 Volt, 222 Amps, 946 Watts, 1600°C
#362MO: Molybdenum, 1.30 Volt, 289 Amps, 376 Watts, 1400°C
#363TA: Tantalum, 3.21 Volt, 319 Amps, 1024 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats Inverted Top Hat Dimple
Dimple Boats

#364MO: Molybdenum, 1.15 Volt, 119 Amps, 137 Watts, 1400°C
#365TA: Tantalum, 3.42 Volt, 97 Amps, 332 Watts, 1600°C
#366W: Tungsten, 3.87 Volt, 140 Amps, 542 Watts, 1800°C
#367MO: Molybdenum, 1.10 Volt, 131 Amps, 144 Watts, 1400°C
#368TA: Tantalum, 2.33 Volt, 130 Amps, 303 Watts, 1600°C
#369W: Tungsten, 2.58 Volt, 187 Amps, 482 Watts, 1800°C
#370W: Tungsten, 2.06 Volt, 245 Amps, 505 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#371W: Tungsten, 3.67 Volt, 188 Amps, 690 Watts, 1800°C
#372MO: Molybdenum, 1.58 Volt, 249 Amps, 393 Watts, 1400°C
#373TA: Tantalum, 3.35 Volt, 281 Amps, 941 Watts, 1600°C
#374W: Tungsten, 2.82 Volt, 269 Amps, 759 Watts, 1800°C
#375MO: Molybdenum, 1.27 Volt, 310 Amps, 394 Watts, 1400°C
#376W: Tungsten, 2.57 Volt, 508 Amps, 1306 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Inverted Top Hat Well
Dimple Boats
Inverted Top-Hat Well

#377MO: Molybdenum, 1.39 Volt, 105 Amps, 146 Watts, 1400°C
#378TA: Tantalum, 2.61 Volt, 120 Amps, 313 Watts, 1600°C
#379W: Tungsten, 2.71 Volt, 155 Amps, 420 Watts, 1800°C
#380MO: Molybdenum, 0.92 Volt, 149 Amps, 138 Watts, 1400°C
#381TA: Tantalum, 2.01 Volt, 156 Amps, 314 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats Inverted Top Hat Wide Dish
Dimple Boats

#382W: Tungsten, 4.59 Volt, 372 Amps, 1707 Watts, 1800°C
#383MO: Molybdenum, 1.52 Volt, 317 Amps, 482 Watts, 1400°C
#384TA: Tantalum, 3.48 Volt, 338 Amps, 1176 Watts, 1600°C
#385W: Tungsten, 3.53 Volt, 531 Amps, 1874 Watts, 1800°C
#386MO: Molybdenum, 1.22 Volt, 389 Amps, 475 Watts, 1400°C
#387W: Tungsten, 2.91 Volt, 654 Amps, 1903 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Notched Dimple
Dimple Boats

#388MO: Molybdenum, 1.95 Volt, 78 Amps, 152 Watts, 1400°C
#389TA: Tantalum, 4.44 Volt, 92 Amps, 408 Watts, 1600°C
#390W: Tungsten, 4.96 Volt, 136 Amps, 675 Watts, 1800°C
#391MO: Molybdenum, 1.33 Volt, 112 Amps, 149 Watts, 1400°C
#392TA: Tantalum, 2.92 Volt, 129 Amps, 377 Watts, 1600°C
#393W: Tungsten, 3.11 Volt, 185 Amps, 575 Watts, 1800°C
#394W: Tungsten, 2.37 Volt, 234 Amps, 555 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#395MO: Molybdenum, 1.92 Volt, 123 Amps, 236 Watts, 1400°C
#396TA: Tantalum, 4.44 Volt, 139 Amps, 617 Watts, 1600°C
#397W: Tungsten, 3.71 Volt, 204 Amps, 757 Watts, 1800°C
#398MO: Molybdenum, 1.40 Volt, 170 Amps, 238 Watts, 1400°C
#399TA: Tantalum, 2.86 Volt, 190 Amps, 543 Watts, 1600°C
#400W: Tungsten, 2.85 Volt, 292 Amps, 832 Watts, 1800°C
#401W: Tungsten, 2.24 Volt, 374 Amps, 838 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats

#402MO: Molybdenum, 1.27 Volt, 241 Amps, 306 Watts, 1400°C
#403TA: Tantalum, 2.97 Volt, 276 Amps, 820 Watts, 1600°C
#404W: Tungsten, 2.99 Volt, 387 Amps, 1157 Watts, 1800°C
#405MO: Molybdenum, 1.07 Volt, 300 Amps, 321 Watts, 1400°C
#406TA: Tantalum, 2.37 Volt, 337 Amps, 799 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats

#408TA: Tantalum, 2.97 Volt, 262 Amps, 778 Watts, 1600°C
#409W: Tungsten, 2.94 Volt, 378 Amps, 1111 Watts, 1800°C
#410MO: Molybdenum, 1.11 Volt, 300 Amps, 333 Watts, 1400°C
#411TA: Tantalum, 2.37 Volt, 325 Amps, 770 Watts, 1600°C
Dimple Boats

#412W: Tungsten, 3.94 Volt, 261 Amps, 1028 Watts, 1800°C
#413MO: Molybdenum, 1.29 Volt, 236 Amps, 304 Watts, 1400°C
#414W: Tungsten, 3.03 Volt, 372 Amps, 1127 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Top Hat Dimple
Dimple Boats

#415MO: Molybdenum, 1.72 Volt, 86 Amps, 148 Watts, 1400°C
#416TA: Tantalum, 3.37 Volt, 100 Amps, 337 Watts, 1600°C
#417W: Tungsten, 3.85 Volt, 140 Amps, 539 Watts, 1800°C
#418MO: Molybdenum, 1.13 Volt, 130 Amps, 147 Watts, 1400°C
#419W: Tungsten, 2.57 Volt, 185 Amps, 475 Watts, 1800°C
#420W: Tungsten, 2.20 Volt, 242 Amps, 532 Watts, 1800°C
Dimple Boats Well
Dimple Boats

#421MO: Molybdenum, 1.32 Volt, 100 Amps, 132 Watts, 1400°C
#422TA: Tantalum, 2.72 Volt, 106 Amps, 288 Watts, 1600°C
#423MO: Molybdenum, 0.9 Volt, 158 Amps, 142 Watts, 1400°C
#424TA: Tantalum, 1.95 Volt, 165 Amps, 322 Watts, 1600°C
Frequently Asked Questions
What are boat sources in thermal evaporation?
Boat sources are typically made from high-purity tungsten, tantalum, or molybdenum due to their high melting points, low vapor pressures, and durability under high thermal loads. In some cases, an alumina coating is applied to prevent wetting or alloying with the evaporant.
What materials are commonly used to fabricate boat sources?
Metal powders are widely used in industries such as automotive (for brake pads and engine components), aerospace, electronics, batteries, capacitors, magnetic materials, and tooling.
How do boat sources differ from crucibles in evaporation systems?
Unlike crucibles that often use a separate heater and may provide larger volumes for thick films, boat sources integrate the heating element with the evaporant container. Boats are especially suitable for upward evaporation and offer faster heating and more controlled deposition for thinner films.
What factors should be considered when selecting a boat source?
Key considerations include the type of evaporant material, boat material compatibility, required evaporation rate, power supply (voltage and current demands), boat geometry (such as dimpled or trough designs), and whether corrosion or wetting issues need to be minimized via coatings.
What advantages do alumina-coated boat sources offer?
Alumina coatings on boat sources help prevent the molten evaporant from “wetting” the entire source, which can lead to non-uniform deposition and early failure. The inert alumina layer minimizes chemical reactions and migration of the material, leading to improved film uniformity and extended boat life.
How is the evaporation rate controlled using boat sources?
The evaporation rate is primarily controlled by adjusting the electrical current supplied to the boat. The increased current raises the boat’s temperature, which in turn increases the vapor pressure of the evaporant. Fine tuning the current allows precise control over the film thickness and deposition rate.
What challenges are associated with boat source evaporation?
Common challenges include material wetting or creeping (which can lead to contamination and loss of material), alloying between the evaporant and boat material (especially for reactive metals), and the need for high power input. Proper design and coating strategies are critical to mitigate these issues.
How do boat source designs vary?
Boat sources come in various designs—such as dimpled, trough, or flat configurations—to optimize the hot zone where the material melts. Some designs include isolated hot zones or directional features to control evaporation patterns and improve film uniformity.
Can boat sources be used for a wide range of materials?
Yes. Boat sources are versatile and can be used to evaporate many metals, alloys, and even some compound materials. However, material-specific considerations (e.g., reactivity and melting point) may require selecting a particular boat material or applying an alumina coating to ensure successful deposition.
What maintenance practices ensure the longevity of a boat source?
To extend the life of a boat source, it’s important to operate within its specified power range, avoid overfilling with evaporant, and use proper cooling periods between runs. Regular inspection for signs of wear or contamination and replacing boats when necessary are also key practices.
How do boat sources impact the uniformity of the deposited film?
The geometry of the boat (e.g., whether it’s dimpled or has a trough design) influences the distribution of heat and the vapor flux. A well-designed boat source provides a concentrated hot zone that promotes a uniform evaporation rate, leading to more even thin film deposition on the substrate.
What troubleshooting steps can be taken if a boat source fails prematurely?
If a boat source fails, check for issues such as excessive wetting or alloying of the evaporant with the boat material, incorrect power settings, or overfilling. Adjusting the current, using an alumina-coated boat, or selecting an alternative material may resolve the problem.