Helium leak detectors are essential tools used in various industries to identify and locate leaks in systems where maintaining airtight or vacuum conditions is critical. Whether in high-tech industries like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, or electronics, even the tiniest leaks can have severe consequences on performance, safety, and cost. In this article, we’ll explore the principles behind helium leak detection, the different methods employed by these detectors, and the wide range of applications where this technology is indispensable. Additionally, we will discuss the advantages and challenges of using helium for leak detection, offering a comprehensive understanding of how these detectors work and why they are so effective.
The Importance of Leak Detection
Leaks can occur in a wide range of systems, including pressurized vessels, vacuum chambers, gas lines, and refrigeration systems. They can lead to a variety of issues, such as equipment failure, compromised safety, environmental harm, and loss of valuable resources. For instance, in semiconductor manufacturing, even the smallest leak in a vacuum chamber can result in contamination, rendering the entire process ineffective and costly. In aerospace, leaks in fuel systems or pressurized cabins can be catastrophic.
To mitigate these risks, industries employ leak detection methods, and one of the most effective ways is through the use of helium leak detectors. Helium, with its distinct properties, serves as a reliable tracer gas that can detect leaks so small they might otherwise go unnoticed.
The Science Behind Helium Leak Detection
Helium is ideal for leak detection due to its unique properties. It is an inert, non-toxic, and non-flammable gas that does not react chemically with the materials being tested. Furthermore, helium has one of the smallest atomic sizes of any element, allowing it to pass through even the tiniest leaks. The low concentration of helium in the atmosphere (around 5 parts per million) ensures that any detected helium is likely to have come from the system being tested, rather than from background air.
The process of helium leak detection is based on these fundamental principles. When helium is introduced into a system under test, it will escape through any existing leaks. A helium leak detector is designed to identify and quantify this escaping helium, giving an accurate measurement of the leak’s size and location.
Key Components of a Helium Leak Detector
A helium leak detector consists of several critical components that work together to detect the presence of helium. These include:
- Vacuum Pump: The first step in the detection process is creating a vacuum within the system to be tested. A vacuum pump is used to reduce the air pressure, creating an environment where leaks can be detected more easily. It ensures that the gas can be drawn through the system and into the detector.
- Mass Spectrometer: This is the core technology behind most helium leak detectors. The mass spectrometer is a highly sensitive device that can detect individual molecules of helium in a gas mixture. When helium enters the mass spectrometer, it is ionized, and the ions are separated according to their mass-to-charge ratio. The detector then measures the amount of helium present, giving an accurate indication of the leak rate.
- Sniffer Probe: For localized leak detection, a sniffer probe is often used. This handheld device is equipped with a sensor that can detect helium as it escapes from a system. It is useful for pinpointing leaks in larger systems or for testing areas where vacuum chambers are not practical.
- Control System: The control system is responsible for processing the data from the mass spectrometer and providing the operator with real-time readings. Modern helium leak detectors often come with advanced software that allows users to set leak rate thresholds, visualize data, and analyze results.
- Helium Source: To test the system, helium gas is introduced either externally or directly into the system under test. The helium can be supplied from a bottle or a helium generator, depending on the size and nature of the leak testing.
How Helium Leak Detectors Work
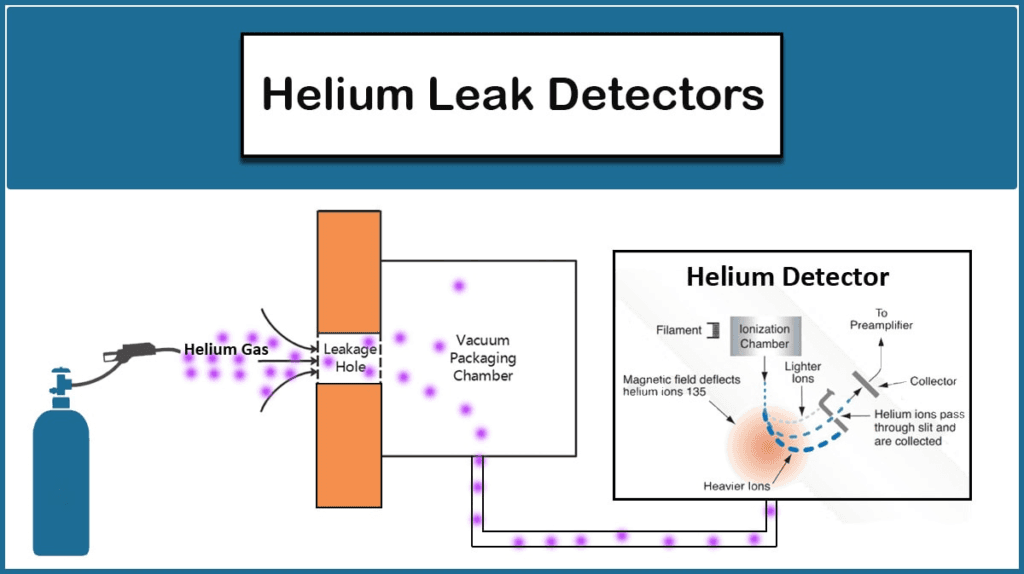
Helium leak detectors work by taking advantage of helium’s ability to escape through leaks in a system. The detection process typically involves two primary methods: the vacuum method and the sniffing method.
Vacuum Method
The vacuum method is the most common technique used for helium leak detection. The process involves evacuating the system to be tested, which creates a vacuum environment. Once the system is under vacuum, helium is introduced around the external surface of the system. If there are any leaks, helium will pass through the small openings, penetrate the system, and be drawn into the mass spectrometer.
The mass spectrometer analyzes the helium and provides a reading that correlates to the leak rate. The leak rate is typically measured in units of mbar·L/s, which represents the volume of helium that leaks per second. The lower the leak rate, the more reliable the system is considered to be.
Sniffing Method
The sniffing method is used when it is impractical to evacuate the system, such as in cases involving large or complex equipment. In this method, helium is introduced into the system being tested, and a sniffer probe is used to detect escaping helium. The probe is passed over potential leak sites, and when helium is detected, the probe alerts the operator. This method is particularly useful for leak detection in large systems, such as pipelines, air conditioning units, or aircraft fuselages.
Calibration and Sensitivity
For accurate and reliable results, helium leak detectors need to be calibrated regularly. Calibration is the process of verifying the accuracy of the detector by testing it against known helium leak rates. This ensures that the detector can consistently identify and quantify leaks within the desired sensitivity range.
Modern helium leak detectors are capable of detecting leaks as small as 10⁻¹² mbar·L/s, which is equivalent to a very tiny volume of helium escaping per second. This level of sensitivity is essential in industries where even the smallest leaks can have significant consequences. For example, in semiconductor manufacturing, a leak of even a few molecules of helium can cause defects in delicate processes like chemical vapor deposition or etching.
Applications of Helium Leak Detectors
Helium leak detectors are used in a wide range of industries, where maintaining sealed, airtight, or vacuum systems is critical. Some of the most prominent applications include:
Aerospace

In the aerospace industry, helium leak detectors are used to test the integrity of fuel tanks, pressure vessels, life-support systems, and other critical components. For example, spacecraft are subject to extreme pressure and temperature conditions, making leak detection an essential part of the design and maintenance process. Even the smallest leak could compromise the integrity of the system and lead to catastrophic failures.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In semiconductor manufacturing, helium leak detectors are used to test vacuum chambers and equipment used in processes like etching and deposition. Semiconductor devices require ultra-clean environments, and leaks can lead to contamination, affecting product yields and performance. Helium leak detectors ensure that vacuum systems remain leak-free, providing a stable environment for precision manufacturing.
Medical Equipment
Helium leak detectors are used in the medical field to ensure the integrity of devices such as pacemakers, catheters, and respiratory equipment. For example, a leak in a pacemaker’s hermetic seal could lead to the introduction of contaminants, affecting the device’s performance and safety. Using helium leak detection allows manufacturers to ensure the reliability and safety of life-critical devices.
Nuclear Industry
In the nuclear industry, helium leak detectors are used to check the integrity of reactor pressure vessels, gas storage systems, and other critical infrastructure. The smallest leaks in these systems can result in hazardous situations, including contamination of the surrounding environment. Helium leak detectors are used to ensure these systems maintain their integrity under extreme conditions.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry also uses helium leak detectors to test components such as air conditioning systems, fuel systems, and tire pressure monitoring systems. Leaks in these components can lead to inefficiency, safety risks, and increased operating costs. By detecting leaks early in the manufacturing process, companies can avoid costly repairs and enhance the performance of their products.
Advantages of Using Helium as a Tracer Gas
Helium is the preferred tracer gas in leak detection due to several key advantages:
- Inert and Non-Reactive: Unlike hydrogen or other gases, helium does not react with the materials being tested, ensuring that it won’t alter the integrity of the system being examined.
- Small Molecular Size: Helium has one of the smallest atomic radii, allowing it to pass through even the tiniest cracks or pores. This makes it ideal for detecting microscopic leaks that might go unnoticed with other methods.
- Low Background Concentration: Because helium is rare in the atmosphere, its presence in a tested system can be easily detected without interference from ambient air.
- Safety: Helium is non-toxic, non-flammable, and poses no risk to human health or the environment. This makes it a safe option for leak testing in industries where safety is a top priority.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many advantages, there are some challenges associated with using helium leak detectors. One of the primary concerns is the cost of helium, which has increased in recent years due to supply and demand constraints. In some cases, large-scale testing can become expensive due to the cost of the gas.
Additionally, helium leak detectors require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure their accuracy. Without proper calibration, the detector may provide false readings, leading to incorrect leak assessments. Additionally, helium leak detectors require skilled operators to interpret the results and make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Helium leak detectors are indispensable tools in many industries where even the smallest leak can lead to significant consequences. By using helium as a tracer gas, these detectors are able to identify leaks with remarkable sensitivity and accuracy. Whether in aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, medical devices, or other critical applications, helium leak detection plays a vital role in maintaining system integrity and ensuring safety. Despite the challenges of cost and maintenance, the benefits of using helium for leak detection far outweigh the drawbacks, making it a trusted technology for industries worldwide.



1 thought on “How Does a Helium Leak Detector Work?”
Merely wanna comment on few general things, The website design is perfect, the written content is very good : D.