A chamber furnace is a specialized type of industrial oven used for heat treatment processes. It is designed to create a controlled thermal environment in which materials can be heated, tempered, annealed, or processed in other ways that require precise temperature control. Chamber furnaces are widely utilized in industries ranging from metalworking and manufacturing to research and development, and they play an essential role in shaping the properties of materials through heat.
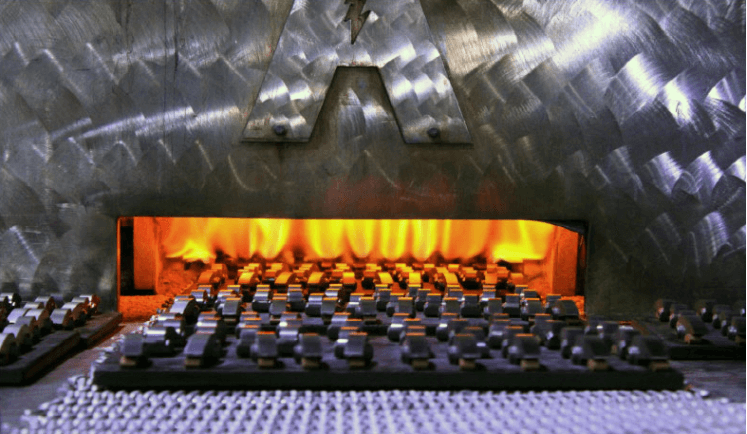

Sintering is a method used to form solid materials from powders by heating them to below their melting point. In the chamber furnace, powder particles are fused together by heat to create a more solid, durable object. This process is commonly used for manufacturing ceramic products, as well as certain types of metal parts, like filters and porous components. Sintering helps materials achieve higher density and mechanical strength.
3. Drying and Baking
Furnaces are also commonly used for drying and baking materials. In this context, a chamber furnace can be used to remove moisture from materials, cure coatings, or harden adhesives. This is particularly important in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and ceramics, where precise control of temperature and humidity is essential for product quality.
For instance, in the production of ceramics, the drying process involves slowly heating the raw ceramic products to remove moisture and avoid cracking. Similarly, in the food industry, drying furnaces can help remove water from products like fruits and vegetables while preserving their nutritional content.
4. Fusing Materials
Chamber furnaces are also used for fusing materials such as glass or certain types of metal alloys. Fusing involves heating materials to the point where they melt and fuse together. For example, in the glass industry, a chamber furnace is often used to melt and shape glass into specific forms, such as glassware or windows.
Similarly, in the metalworking industry, a chamber furnace may be used to melt and fuse metals for casting and molding processes. The precise control of temperature within the furnace is crucial to ensuring the correct melting point and optimal properties of the final product.
5. Brazing and Welding
Brazing and welding are processes used to join two pieces of material, typically metals, through the application of heat. In brazing, a filler material is melted and used to join metal pieces. In welding, the base materials themselves are melted and fused together.
Chamber furnaces can play a key role in both of these processes, particularly when they are used to heat materials to the necessary temperatures without causing oxidation or damage to the components. The controlled environment of a chamber furnace ensures that heat is evenly distributed and that the workpieces remain free from contaminants during the process.
6. Curing of Polymers and Coatings
The curing process involves using heat to chemically alter a material, usually a polymer or resin, in order to make it stronger or more stable. A chamber furnace is particularly useful for curing coatings, such as paints or adhesives, applied to metal, plastic, or other substrates.
For example, the automotive industry relies on chamber furnaces to cure protective coatings on car parts, ensuring that they are durable and resistant to wear, heat, and chemicals. Similarly, in the electronics industry, heat-curing is essential to ensuring the integrity and performance of components such as circuit boards.
7. Research and Development
In research laboratories, chamber furnaces are invaluable tools for experimentation and material analysis. They provide a controlled environment in which scientists and engineers can investigate the effects of heat on various materials, conduct testing for new manufacturing processes, or evaluate new materials for industrial applications.
In material science, for example, a chamber furnace might be used to simulate extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, to study how materials react under stress. This can be essential for advancing technology in fields like aerospace engineering, automotive manufacturing, and even energy production.
8. Controlled Atmosphere Heat Treatment
Some chamber furnaces are equipped with the ability to control the atmosphere inside the furnace. This is especially important for processes that require an inert or specific gas environment. For example, during the vacuum heat treatment process, the furnace chamber is evacuated of air to prevent oxidation. The furnace might also be filled with inert gases such as nitrogen or argon to prevent contamination during the heating process.
This controlled atmosphere feature is crucial in industries where materials must be treated without exposure to oxygen or moisture, such as in the production of high-performance alloys or in the semiconductor industry.
Conclusion
A chamber furnace is a vital piece of equipment across many industries, providing controlled, high-temperature environments for heat treatment, sintering, drying, fusing, brazing, curing, and more. The versatility and precision of chamber furnaces make them indispensable for both industrial and laboratory applications, ensuring that materials are processed to meet the stringent requirements of various manufacturing and research processes.
By understanding the key functions and applications of chamber furnaces, businesses can optimize their production processes, enhance the quality of their products, and innovate in areas that require precise temperature control. Whether used for material testing, production, or scientific experimentation, the chamber furnace plays an essential role in modern industry.



