Gate valves are critical components in fluid control systems, commonly used in various industries to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. They operate by raising or lowering a gate or wedge to either allow unobstructed flow or create a tight seal to stop the flow entirely. These valves are highly versatile and suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, making them indispensable in industries like oil and gas, water management, power generation, and chemical processing. This article explores the detailed applications, types, and benefits of gate valves, focusing on their widespread usage across multiple sectors.
Key Features of Gate Valves
Gate valves are known for their simple design and reliable operation. They feature a linear motion mechanism where the gate moves vertically to control flow. When fully open, they provide minimal resistance and allow maximum flow, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal pressure drop. The tight seal they create when closed ensures leak-proof performance, which is crucial in systems handling hazardous or expensive fluids. Additionally, gate valves are available in different materials and configurations, allowing customization for specific fluid types, temperatures, and pressures.
How Gate Valves Operate
The operation of a gate valve involves the vertical movement of a gate controlled by a handwheel, lever, or actuator. When the valve is fully open, the gate retracts entirely into the bonnet, leaving a straight, unobstructed flow path. When closed, the gate seats tightly against the valve body, creating a barrier that prevents fluid movement. This straightforward mechanism ensures durability and efficiency in on/off applications but is not suitable for throttling, as partial openings can cause wear and turbulence.
Applications in Water Distribution Systems
In municipal water systems, gate valves are integral for isolating sections of the network during maintenance or emergencies. They are often installed at strategic points in pipelines to control the flow of water in residential, commercial, and industrial areas. Their ability to handle high volumes and pressures makes them ideal for ensuring consistent water supply and managing flow disruptions.
Role in Wastewater Management
Gate valves are also extensively used in wastewater treatment facilities to control the flow of effluents and sludge. Their robust design allows them to handle abrasive and corrosive materials, ensuring smooth operation even under challenging conditions. Specialized variants, such as knife gate valves, are particularly effective in cutting through thick slurry, making them invaluable in sewage systems.
Oil and Gas Industry Applications
Gate valves are indispensable in the oil and gas sector for managing the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and other hydrocarbons. Their ability to operate under high pressures and temperatures ensures safe and efficient transportation in pipelines, refineries, and storage facilities. They are commonly used in wellhead assemblies, processing plants, and offshore platforms, where reliability and durability are paramount.
Use in Power Generation Facilities

Power plants, especially those relying on steam generation, utilize gate valves to control the flow of steam and cooling water. These valves are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, ensuring safe and efficient operation in thermal and nuclear power stations. Their leak-proof seal is critical in preventing steam loss, which can affect energy efficiency and safety.
Chemical Processing Applications
Gate valves are widely used in the chemical industry for handling aggressive and corrosive fluids. Their robust construction and the availability of materials like stainless steel and specialty alloys make them ideal for applications requiring resistance to harsh chemicals and high temperatures. In chemical plants, gate valves ensure precise flow control and prevent cross-contamination between different fluid streams.
Mining and Mineral Processing
In mining operations, gate valves manage the flow of slurry, tailings, and other abrasive materials. Knife gate valves, in particular, are designed to cut through dense materials, making them ideal for use in pipelines carrying mixtures of solids and liquids. Their rugged construction ensures reliable performance in the demanding environments of mining and mineral processing.
Types of Gate Valves
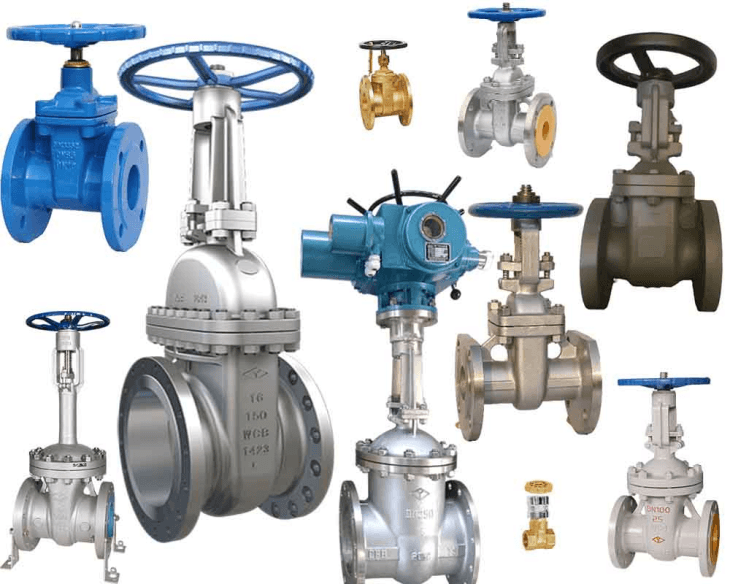

Gate valves are available in various designs, each tailored to specific applications. Rising stem gate valves feature a visible stem that moves up and down, providing an easy way to determine the valve’s position. Non-rising stem valves, on the other hand, are compact and suited for underground or space-constrained installations. Wedge gate valves offer excellent sealing capabilities, making them ideal for high-pressure systems, while parallel gate valves are preferred for their low friction and wear in abrasive applications. Knife gate valves are specifically designed to handle slurry and thick fluids, making them a staple in wastewater and mining industries.
Advantages of Gate Valves
Gate valves offer numerous benefits, including minimal pressure drop when fully open, tight sealing when closed, and compatibility with a wide range of fluids. Their durability and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures make them suitable for demanding applications. Additionally, their straightforward design ensures ease of operation and maintenance, contributing to their widespread use across industries.
Limitations of Gate Valves
Despite their advantages, gate valves have some limitations. They are not suitable for throttling applications, as partial openings can cause turbulence and damage the sealing surfaces. Their slow operation compared to other valve types may not be ideal for applications requiring rapid flow control. Furthermore, the presence of debris in the fluid can obstruct the gate’s movement, leading to potential operational issues.
Installation and Maintenance of Gate Valves
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for the reliable performance of gate valves. During installation, ensuring correct alignment and support is critical to prevent stress on the valve body. Routine inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. Lubricating the stem and other moving parts helps maintain smooth operation, while periodic testing ensures the valve’s functionality. Following manufacturer guidelines for maintenance can significantly extend the service life of gate valves.
Emerging Trends in Gate Valve Technology
Advancements in materials and technology are driving innovations in gate valve design. The use of corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings enhances durability in harsh environments, while the integration of smart technology enables remote monitoring and control. Compact designs and lightweight materials are also being developed to improve installation and handling, making gate valves more versatile than ever.
Conclusion
Gate valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering reliable performance in a wide range of applications. Their ability to provide an unobstructed flow or a tight seal makes them ideal for industries such as water management, oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. Understanding the types, advantages, and limitations of gate valves allows for their optimal selection and use in various industrial settings. With ongoing advancements in materials and technology, gate valves continue to evolve, meeting the demands of modern fluid control systems while maintaining their reputation for reliability and efficiency.