Enabling Stable, Clean, and Reproducible Thermal Evaporation Processes
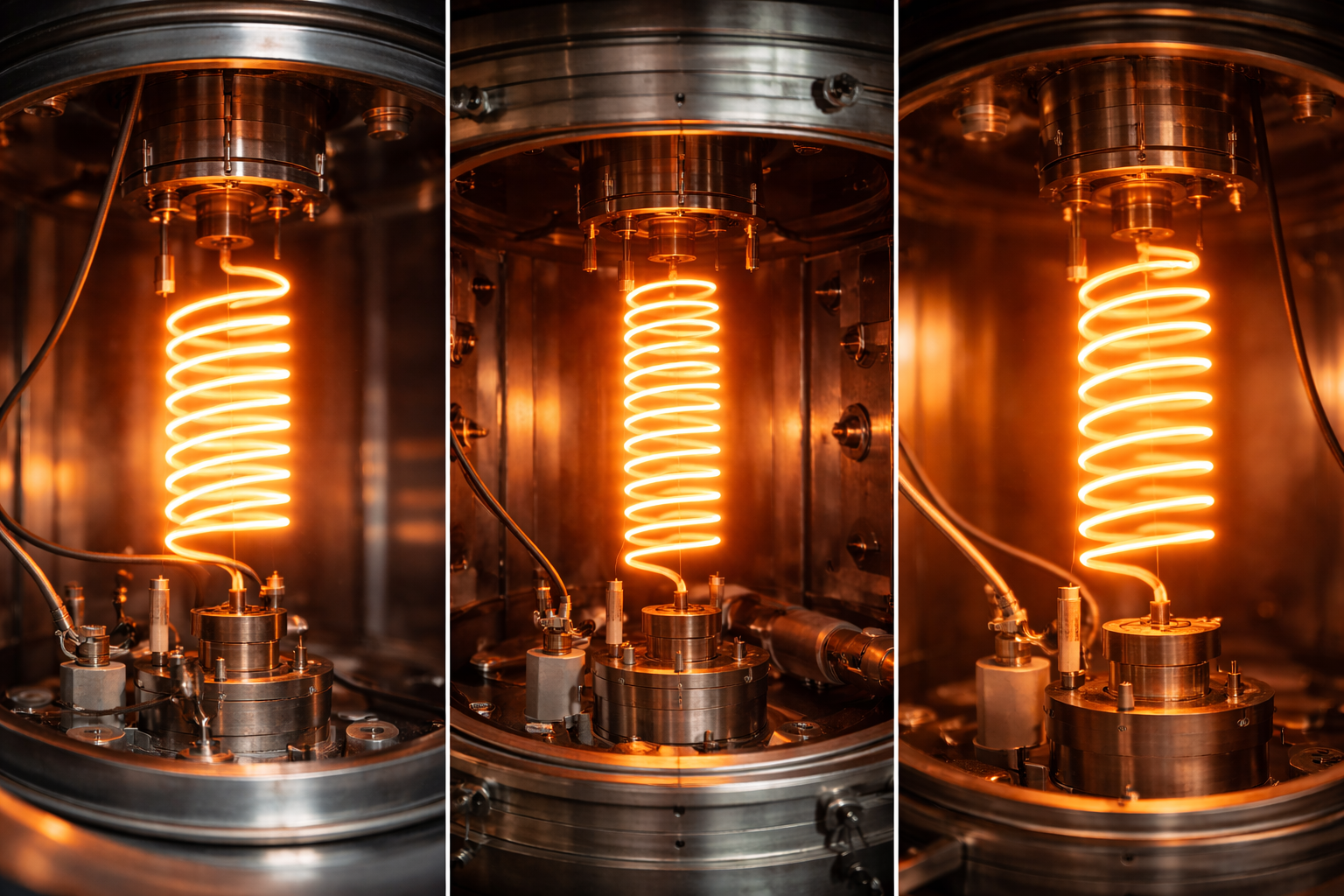
Thermal evaporation remains one of the most widely adopted physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques in thin-film manufacturing, despite the rapid evolution of sputtering and advanced plasma-based methods. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with a broad range of materials make it indispensable in both research laboratories and industrial production lines. At the heart of every thermal evaporation system lies a deceptively simple yet critically important component: the thermal filament tungsten coil.
High-quality thermal filament tungsten coils are not merely consumables. They directly influence evaporation stability, deposition rate control, film purity, thickness uniformity, and overall process reliability. For Thin Film Materials (TFM), delivering premium tungsten filament coils is a foundational part of supporting advanced thin-film technologies across optics, semiconductors, electronics, and scientific research.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of high-quality thermal filament tungsten coils, covering material fundamentals, design considerations, manufacturing quality factors, performance advantages, application scenarios, and selection guidelines—demonstrating why tungsten coils remain essential in modern thin-film deposition systems.
1. Role of Thermal Filament Tungsten Coils in Thin-Film Deposition
1.1 Core Function in Thermal Evaporation Systems
In a thermal evaporation setup, electrical current passes through a filament, converting electrical energy into heat through resistive heating. The filament temperature rises rapidly under high vacuum, enabling the evaporation or sublimation of source materials loaded onto or in contact with the filament.
The tungsten coil performs multiple simultaneous roles:
- High-temperature heating element
- Mechanical support for evaporation materials
- Electrical conductor with predictable resistance
- Thermal structure maintaining geometric integrity
Any instability in filament performance can cause fluctuations in evaporation rate, material spitting, non-uniform film thickness, or premature failure of the evaporation source.
1.2 Why Filament Quality Matters More Than Expected
Although thermal evaporation appears straightforward, it is extremely sensitive to subtle variations in filament behavior. Inconsistent filament geometry, uneven resistivity, or contamination can lead to:
- Unstable evaporation rates
- Difficulty in achieving precise thickness control
- Increased particle generation
- Contamination of deposited films
- Reduced reproducibility between runs
For high-value thin films—particularly in optical coatings and semiconductor layers—these issues are unacceptable. High-quality tungsten filament coils are therefore essential, not optional.
2. Why Tungsten Is the Preferred Filament Material
2.1 Exceptional Melting Point and Thermal Endurance
Tungsten has the highest melting point of all pure metals, approximately 3422°C. This extreme thermal capability allows tungsten filaments to operate safely at temperatures required for evaporating a wide range of materials without softening, sagging, or structural collapse.
This property is particularly important for:
- High-power evaporation
- Repeated thermal cycling
- Long deposition runs
2.2 Extremely Low Vapor Pressure
At elevated temperatures, tungsten exhibits an exceptionally low vapor pressure. This minimizes the risk of tungsten atoms evaporating and incorporating into the deposited film.
For applications requiring ultra-high purity—such as semiconductor metallization or optical interference coatings—this low vapor pressure is a decisive advantage.
2.3 Superior High-Temperature Mechanical Strength
Unlike many metals that become ductile or mechanically unstable at high temperatures, tungsten maintains significant tensile strength and creep resistance. This ensures that coil geometry remains stable during operation, preserving uniform heating and evaporation behavior.
3. Key Quality Parameters of High-Quality Tungsten Filament Coils
3.1 Tungsten Purity and Chemical Composition
Purity is the foundation of filament performance. High-quality tungsten filament coils typically use ≥99.95% (3N5) purity tungsten, with tightly controlled trace impurities.
Excessive impurities such as oxygen, carbon, iron, or nickel can lead to:
- Localized hot spots
- Brittle fracture
- Accelerated grain growth
- Reduced filament lifetime
TFM emphasizes strict raw material qualification to ensure chemical stability and consistency across production batches.
3.2 Wire Diameter Accuracy and Electrical Consistency
The diameter of tungsten wire directly determines electrical resistance, heating efficiency, and current requirements. Even small deviations in wire diameter can cause significant differences in operating temperature.
High-quality tungsten coils are characterized by:
- Tight diameter tolerances
- Uniform resistivity along the wire length
- Consistent electrical behavior between coils
This consistency allows users to replicate evaporation recipes with confidence.
3.3 Grain Structure and Metallurgical Control
The microstructure of tungsten wire plays a major role in filament durability. Controlled grain orientation and grain size help prevent:
- Grain boundary cracking
- Excessive recrystallization
- Sudden mechanical failure
Optimized heat treatment and annealing processes are essential to achieving this microstructural stability.
4. Coil Design and Structural Considerations
4.1 Common Tungsten Filament Coil Configurations
Different evaporation requirements call for different filament geometries. Common designs include:
- Single-loop filaments – Simple geometry for small-scale evaporation
- Helical coils – Improved material retention and heating uniformity
- Basket coils – Suitable for higher material loading and more uniform evaporation
- Custom-shaped filaments – Designed for specific crucible-less evaporation needs
Each configuration influences heat distribution, evaporation rate, and material utilization efficiency.
4.2 Mechanical Stability Under High Temperature
A high-quality tungsten coil must maintain its shape even at extreme operating temperatures. Poorly manufactured coils may suffer from:
- Coil collapse
- Uneven spacing between turns
- Material slippage
- Electrical shorting
Precision forming and stress-relief processes are essential to long-term mechanical integrity.
4.3 Surface Finish and Cleanliness
Surface condition significantly affects filament performance. Smooth, clean tungsten surfaces reduce contamination risks and improve thermal uniformity.
High-quality coils undergo cleaning processes to remove:
- Drawing lubricants
- Oxide residues
- Particulates
This is especially critical for ultra-high vacuum (UHV) applications.
5. Manufacturing Advantages of TFM Tungsten Filament Coils
5.1 Consistent Performance Across Batches
For users operating multiple deposition systems or running production processes, batch-to-batch consistency is critical. TFM emphasizes controlled manufacturing workflows to ensure reproducible electrical and mechanical properties.
5.2 Extended Service Life
Optimized metallurgy and precise forming techniques significantly extend filament lifespan. Longer service life translates to:
- Reduced downtime
- Lower consumable costs
- Increased process stability
This is particularly valuable in production environments where frequent filament replacement disrupts throughput.
5.3 Stable and Predictable Evaporation Rates
Uniform heating enables smoother evaporation rate profiles, allowing tighter thickness control and better film uniformity. This is essential for multilayer optical coatings and precision electronic films.
6. Compatibility with a Wide Range of Evaporation Materials
High-quality tungsten filament coils are compatible with numerous evaporation materials, including:
- Noble metals: Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Platinum (Pt)
- Base metals: Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni)
- Low-melting oxides
- Organic materials for OLED and optoelectronic devices
By adjusting coil geometry, wire diameter, and operating power, tungsten filaments can be optimized for different materials and deposition conditions.
7. Application Areas

7.1 Optical Coatings
In optical thin films, uniformity and purity are paramount. Tungsten filament coils enable stable evaporation for:
- Reflective coatings
- Anti-reflection layers
- Infrared and ultraviolet optical films
7.2 Semiconductor and Microelectronics
Thermal evaporation remains widely used for metallization, seed layers, and contact layers. High-purity tungsten coils help minimize contamination and improve device reliability.
7.3 Research and Laboratory Deposition
Universities and research institutes value tungsten filament coils for their simplicity, versatility, and reliability in experimental thin-film studies.
7.4 Emerging Applications
Advanced applications such as flexible electronics, sensors, and organic electronics continue to rely on thermal evaporation, reinforcing the long-term relevance of tungsten filament technology.
8. Selecting the Right Tungsten Filament Coil
When choosing a thermal filament tungsten coil, users should consider:
- Evaporation material type and melting point
- Required deposition rate and film thickness control
- Power supply limitations and electrical characteristics
- Chamber geometry and source-to-substrate distance
- Standard vs. custom filament requirements
TFM supports both standard specifications and customized filament solutions to meet diverse application needs.
9. Best Practices for Use and Handling
To maximize performance and lifespan:
- Avoid touching filaments with bare hands
- Gradually ramp power during initial heating
- Operate under proper vacuum conditions
- Prevent overloading with excessive source material
Proper handling complements filament quality to achieve optimal deposition outcomes.
10. Conclusion
High-quality thermal filament tungsten coils play a foundational role in thermal evaporation systems. While often overlooked, they directly influence deposition stability, film quality, process reproducibility, and operational efficiency.
Through high-purity tungsten materials, precise manufacturing control, and application-driven design, TFM tungsten filament coils provide reliable performance for demanding thin-film applications across optics, electronics, semiconductors, and research environments.
As thin-film technologies continue to evolve, the importance of stable, clean, and reproducible evaporation sources remains unchanged. High-quality tungsten filament coils are not just components—they are enablers of precision thin-film engineering.