Lithium Zirconate Sputtering Target Description

Lithium zirconate sputtering target is a black sputtering material composed of lithium and zirconium. This conductive ceramic solid electrolyte material is primarily used in lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium is a chemical element derived from the Greek word ‘lithos,’ meaning stone. It was first identified in 1817 by A. Arfwedson, with its isolation later achieved and announced by W. T. Brande. Represented by the symbol “Li,” lithium holds the atomic number 3 in the periodic table, located at Period 2 and Group 1, within the s-block elements. Its relative atomic mass is approximately 6.941 Daltons, with the number in parentheses indicating a margin of uncertainty.

Zirconium is a chemical element named after the Persian word ‘zargun,’ meaning gold-colored. It was first mentioned in 1789 and observed by H. Klaproth. The isolation was later achieved and announced by J. Berzelius. Represented by the symbol “Zr,” zirconium has an atomic number of 40 in the periodic table, located at Period 5 and Group 4, within the d-block elements. Its relative atomic mass is approximately 91.224 Daltons, with the number in parentheses indicating the uncertainty.
Lithium Zirconate Sputtering Target Specification
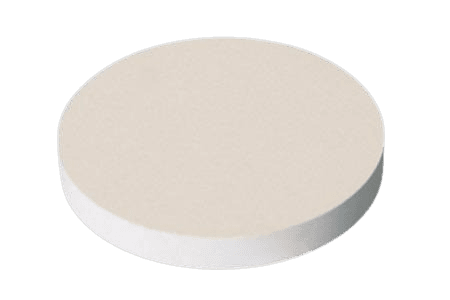
| Material Type | Lithium Zirconate |
| Symbol | LiZrOx |
| Color/Appearance | White Solid |
| Available Sizes | Dia.: 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″, 6.0″ Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″ |
Lithium Zirconate Sputtering Target Packaging
Our lithium zirconate sputtering targets are meticulously tagged and labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. We take great care to prevent any damage during storage and transportation, preserving the quality of our products in their original condition.
Get Contact
TFM offers lithium zirconate Sputtering Targets in various forms, purities, sizes, and prices. We specialize in high-purity thin film deposition materials with optimal density and minimal grain sizes, which are ideal for semiconductor, CVD, and PVD applications in display and optics. Contact Us for current pricing on sputtering targets and other deposition materials that are not listed.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.