Introduction to Nickel Tube
Nickel tube, also known as nickel alloy tubing, is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant metal product widely used in extreme industrial environments. Thanks to nickel’s excellent resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and high temperatures, nickel tubes serve critical roles in aerospace, chemical processing, marine, power generation, and medical applications.
As a versatile product available in various grades and forms, nickel tubes are manufactured with strict adherence to international standards to ensure performance under pressure, temperature, and aggressive chemical conditions.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Nickel
Understanding the core characteristics of nickel helps explain why nickel tubes are so valuable:
- Atomic Number: 28
- Atomic Weight: 58.69 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1455°C (2651°F)
- Density: 8.90 g/cm³
- Magnetic: Yes (ferromagnetic)
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent in both acidic and alkaline environments
- Thermal Conductivity: High, allowing heat transfer in demanding applications
Nickel’s excellent strength and resistance to corrosion make it a prime candidate for manufacturing tubes used in heat exchangers, chemical plants, and nuclear reactors.
Manufacturing Processes of Nickel Tubes
Nickel tubes are fabricated through several advanced metallurgical techniques to meet specific structural and mechanical demands. The main methods include:
1. Seamless Nickel Tubes
Produced via extrusion or rotary piercing, seamless nickel tubes offer a uniform structure with no welds, making them ideal for high-pressure environments. These tubes go through additional cold drawing or pilgering processes to achieve tighter tolerances and better surface finishes.
2. Welded Nickel Tubes
Nickel sheets or coils are rolled and welded using TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or laser welding. After welding, the tubes are annealed and tested for strength and integrity. Welded nickel tubes are cost-effective and suitable for moderate-pressure applications.
3. Cold Drawing
To improve mechanical properties and dimensional precision, tubes are cold-drawn through dies. Cold working increases strength but may reduce ductility unless annealing follows.
4. Annealing
Post-drawing or welding, annealing helps to relieve internal stresses, improve ductility, and restore corrosion resistance.
5. Finishing and Testing
Finishing operations include straightening, pickling, polishing, and ultrasonic testing to ensure the nickel tubes meet ASTM, ASME, or ISO standards.
Common Grades of Nickel Alloys Used in Tubes
Nickel tubes are manufactured from various grades and alloys, each with distinct advantages depending on the application:
| Nickel Alloy | Composition | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel 200 | ≥99.6% Ni | High ductility, excellent for caustic environments |
| Nickel 201 | Low carbon | Improved resistance to graphitization at high temperatures |
| Inconel 600 | Ni-Cr-Fe | Outstanding resistance to oxidation and heat |
| Inconel 625 | Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb | Excellent for seawater and high-stress environments |
| Monel 400 | Ni-Cu | Resistant to saltwater and acids |
| Hastelloy C276 | Ni-Mo-Cr | Withstands strong oxidizing and reducing chemicals |
| Alloy 825 | Ni-Fe-Cr | Acid and alkali resistance in high-temperature environments |
Dimensions and Tolerances
Nickel tubes come in a wide range of sizes:
- Outer Diameter (OD): 1/8” to 12” (3.2 mm to 305 mm)
- Wall Thickness: 0.02” to 0.5” (0.5 mm to 12.7 mm)
- Length: Custom lengths up to 6 meters or coiled
Tubes can be produced to tight tolerances in OD, wall thickness, and roundness based on standards like ASTM B163, B165, B167, and B730.
Applications of Nickel Tubes
1. Aerospace Industry
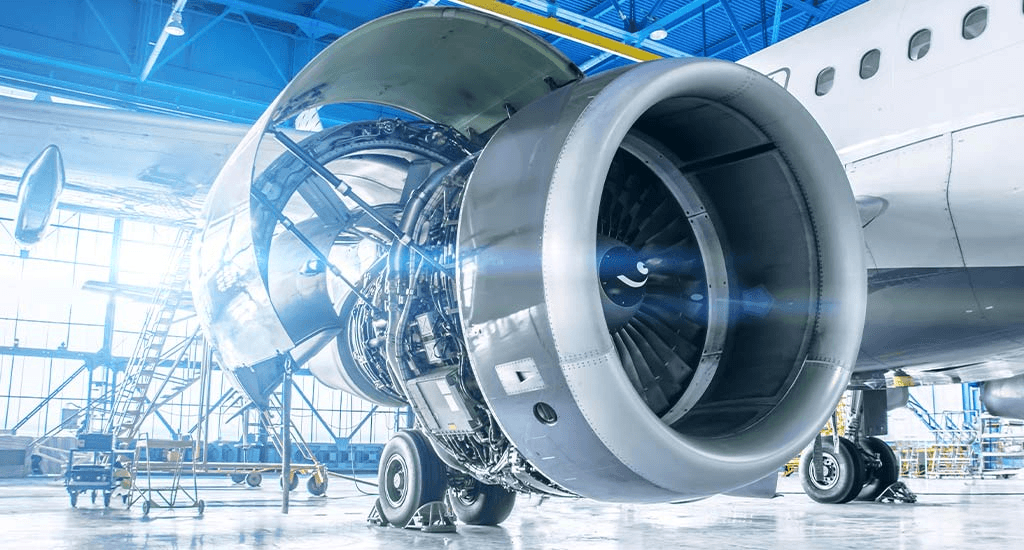
Nickel tubes are used in jet engines, hydraulic systems, and fuel lines due to their heat resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. Alloys like Inconel 718 and 625 perform well under extreme thermal and mechanical stress.
2. Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Tubes made of Monel and Hastelloy resist acidic and caustic environments found in chemical processing. They are used in reactors, condensers, and scrubbers.
3. Power Generation
Nickel tubes are essential in fossil fuel, geothermal, and nuclear power plants. Their ability to withstand high pressures and corrosion makes them ideal for steam generators, condensers, and heat exchangers.
4. Desalination and Marine Applications
Nickel-copper alloys like Monel 400 resist seawater corrosion and are used in desalination plants, offshore platforms, and shipbuilding.
5. Pharmaceutical and Food Industry
Nickel tubes used in these industries are highly polished and conform to sanitary standards. They are used in fluid transfer systems, reactors, and piping exposed to cleaning agents and steam.
6. Electronics and Instrumentation
Due to excellent EMI shielding and chemical stability, nickel tubes serve in sensor casings, thermocouple protection tubes, and electromagnetic shielding components.
Benefits of Nickel Tubes
- High Corrosion Resistance: Especially in reducing and neutral environments.
- Excellent Thermal Stability: Ideal for high-temperature service.
- Good Formability: Easily fabricated through welding, bending, and machining.
- Longevity: Reduced maintenance and long lifecycle.
- Magnetic and Non-magnetic Options: Available based on alloy selection.
- Clean Surface Finish: Critical for semiconductor and pharmaceutical applications.
Global Standards for Nickel Tubes
Nickel tubes must meet strict quality criteria based on the intended use. Some common standards include:
- ASTM B163 / B165: For seamless and welded nickel and nickel alloy tubes for condensers and heat exchangers.
- ASME SB-622 / SB-619: Nickel alloys for high-temperature service.
- ISO 6207: Seamless tubes for nuclear applications.
- EN 10216-5: European standard for seamless steel tubes used in pressure purposes.
Market Trends and Industry Outlook
The nickel tube market is growing steadily, driven by rising demand in renewable energy, aerospace, and chemical processing sectors. The global transition toward hydrogen fuel systems, electric aircraft, and next-gen nuclear reactors has also contributed to increased demand for high-performance nickel alloys.
Key Market Insights:
- Asia-Pacific is the leading consumer, particularly China and India.
- North America sees growth in aerospace and defense.
- Europe is investing in green energy infrastructure.
Rising nickel prices due to supply constraints in Indonesia and geopolitical tensions may impact the market, but innovations in recycling and production efficiency are mitigating these effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between Nickel 200 and 201 tubes?
Nickel 201 has a lower carbon content, making it more suitable for high-temperature applications where graphitization could be a problem. Otherwise, both are commercially pure nickel with excellent corrosion resistance.
2. Are nickel tubes magnetic?
Yes, pure nickel and some nickel alloys like Monel are magnetic, while others such as Inconel may exhibit weak or no magnetism depending on composition and heat treatment.
3. Can nickel tubes be welded?
Yes, nickel tubes are weldable using TIG, MIG, or electron beam welding. The welding technique must match the specific nickel alloy used.
4. What is the typical lifespan of a nickel tube?
When used in the right environment, nickel tubes can last several decades due to their excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
5. Do nickel tubes corrode in seawater?
Nickel-copper alloys like Monel are particularly resistant to seawater corrosion and are commonly used in marine environments.
6. What sizes do nickel tubes come in?
Standard sizes range from 1/8” to 12” OD with custom wall thickness and lengths available.
7. What is the operating temperature range for nickel tubes?
Nickel tubes can operate up to 1000°C (1832°F), depending on the alloy used.
8. Are nickel tubes suitable for cleanroom applications?
Yes, especially those with a polished or electropolished finish, making them suitable for semiconductor and pharmaceutical environments.
9. Can nickel tubing be used for heat exchangers?
Absolutely. Nickel tubes are commonly used in heat exchangers, particularly in corrosive and high-temperature systems.
10. How do I select the right nickel tube alloy?
The choice depends on temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and required mechanical properties. Consult ASTM standards and application-specific guidelines.
11. What certifications should I look for when buying nickel tubes?
ASTM, ASME, ISO, and EN certifications ensure that tubes meet international quality and safety standards.
12. What are the advantages of seamless nickel tubes over welded ones?
Seamless tubes offer superior structural integrity and pressure resistance, making them suitable for critical applications like aerospace or nuclear systems.
Conclusion
Nickel tubes are indispensable in modern engineering due to their excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. From aerospace and power plants to marine and pharmaceutical sectors, nickel tubing plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and performance.
As industries evolve, so does the demand for advanced nickel alloy tubes capable of withstanding harsher environments and higher performance standards. Understanding the types, applications, and benefits of nickel tubes allows engineers and procurement specialists to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.