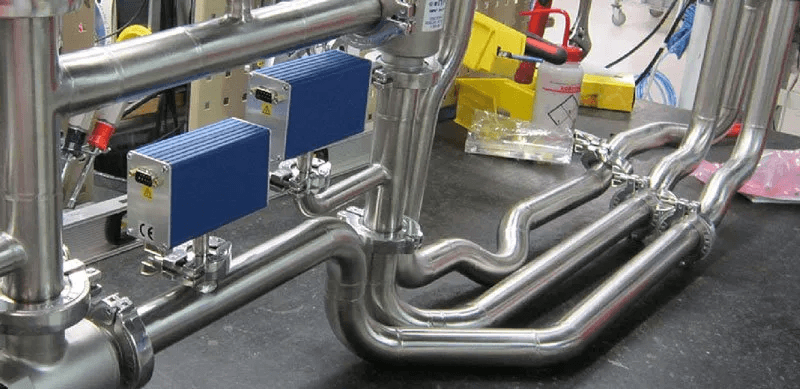
Introduction
In the semiconductor industry, the demand for high-purity, leak-tight, and corrosion-resistant fluid delivery systems is paramount. Weldable fittings play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and performance of these systems, especially in ultra-high purity (UHP) gas lines, chemical delivery systems, and cleanroom environments. Selecting the right weldable fittings is not just about matching sizes; it involves understanding materials, standards, surface finish requirements, and compatibility with semiconductor-grade systems.
This guide will provide a detailed overview of how to select the best weldable fittings for semiconductor applications, enriched with product recommendations from thinfilmmaterials.com to help you make informed purchasing decisions.
Importance of Weldable Fittings in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Semiconductor manufacturing processes such as photolithography, etching, deposition, and chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) require the precise delivery of specialty gases and liquids. Weldable fittings ensure:
- Minimal particle generation
- Zero leak integrity
- Resistance to aggressive chemicals
- Support for high-purity gas delivery
- Long-term system reliability
Any compromise in fittings could lead to contamination, yield loss, costly downtime, or even catastrophic failures.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Weldable Fittings

1. Material Selection
Material purity and compatibility are crucial. The most commonly used materials include:
- 316L Stainless Steel (Electropolished): Standard for UHP gas delivery due to its corrosion resistance and excellent weldability.
- 304 Stainless Steel: Used in less critical areas; slightly lower corrosion resistance compared to 316L.
- Nickel Alloys (e.g., Hastelloy\u00ae): For highly corrosive chemical lines.
Related Product:
When selecting materials, always verify compatibility with the gases or chemicals the line will carry.
2. Dimensional Standards
Follow recognized standards such as:
- SEMI F20: Guide for weld fittings in semiconductor applications.
- ASME BPE: Standard for bioprocessing equipment, often adopted for semiconductor chemical delivery systems.
Consistency in dimensional tolerances ensures proper fit-up and weld quality, critical for leak-free systems.
3. Surface Finish
Surface roughness is a vital factor in contamination control. Smooth internal surfaces minimize particle adhesion and chemical entrapment.
- Electropolished (EP) finishes to a roughness average (Ra) < 10 microinch (0.25 µm) are often required.
- Some extreme purity lines may demand Ra < 5 microinch.
Related Product:
4. Weldability
- Fittings should have consistent wall thickness and straight ends to facilitate orbital welding.
- Material hardness should be within ranges specified for orbital welding to prevent cracking.
- Weld ends should be free from contamination, oxidation, or dimensional inconsistencies.
Orbital welding ensures consistent, high-quality welds critical for ultra-high purity gas systems.
5. Cleanliness and Packaging
Weldable fittings for semiconductor use should be:
- Capped and double-bagged in a cleanroom environment.
- Certified to SEMI F57 or equivalent cleanliness standards.
- Accompanied by documentation including material certificates and surface finish reports.
Proper packaging prevents particulate contamination during storage and transportation.
6. Fitting Types
Depending on the system design, various fitting types are selected:
- Elbows (90\u00b0, 45\u00b0): For directional changes.
- Tees: For branching lines.
- Reducers: For changing tubing diameters.
- Stub Ends: For butt-weld connections to other components.
Related Product:
Selecting the correct configuration minimizes weld joints and dead spaces, improving system purity.
Comparing Weldable Fittings vs. Mechanical Fittings
While mechanical compression fittings (like VCR\u00ae or VCO\u00ae) are also used in semiconductor systems, weldable fittings are preferred when:
- Maximum purity is required.
- Systems operate under extreme vacuum or high pressure.
- Long-term leak-tightness is critical.
Welded joints have no elastomeric seals that could degrade over time, ensuring higher reliability.
| Property | Weldable Fittings | Mechanical Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Purity Level | Highest | Moderate to High |
| Leak Integrity | Superior | Good |
| Installation Flexibility | Low (requires welding) | High (reusable, adjustable) |
| Maintenance Requirement | Minimal | Higher (re-tightening needed) |
Steps for Selecting the Right Weldable Fittings
Step 1: Define the Application Environment
- Identify the chemical/gas type.
- Determine the pressure, temperature, and flow rate requirements.
Step 2: Choose Compatible Material
- For acids: Consider Nickel alloys.
- For standard gases: 316L stainless steel with electropolish.
Step 3: Specify Surface Finish
- Confirm Ra value requirements (typically <10 microinch for UHP lines).
Step 4: Select Dimensions
- Match tube size (OD) and wall thickness to system specifications.
Step 5: Confirm Standards Compliance
- Look for SEMI F20, F57, ASME BPE certifications.
Step 6: Ensure Cleanliness Certification
- Verify factory cleaning process and packaging protocols.
Step 7: Plan for Welding Compatibility
- Ensure fittings are suitable for orbital welding machines (e.g., autogenous GTAW).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mismatching materials: Different alloys between tube and fitting can lead to galvanic corrosion.
- Ignoring surface finish: Rough surfaces trap particles, risking contamination.
- Skipping cleaning verification: Even slight contamination can ruin expensive wafers.
- Choosing cheap, non-certified fittings: Low-cost parts often lack proper documentation and quality control.
Always source from trusted suppliers specializing in semiconductor-grade components.
Why Choose TFM for Weldable Fittings?
thinfilmmaterials.com offers a premium range of weldable elbow fittings, tees, reducers, and stub ends, manufactured from high-purity stainless steel and electropolished to semiconductor standards.
Key Advantages:
- Compliance with SEMI and ASME BPE standards
- Certified surface finishes
- Cleanroom packaging and documentation
- Custom fabrication services for non-standard configurations
Related Products:
Partnering with TFM ensures quality, traceability, and consistent performance across your critical fluid handling systems.
Conclusion
Selecting the best weldable fittings for semiconductor equipment involves a detailed understanding of material compatibility, cleanliness standards, surface finish requirements, and welding processes. Careful selection ensures the purity and integrity of fluid and gas delivery systems, directly impacting semiconductor yield and operational efficiency.
By sourcing high-quality weldable fittings from trusted suppliers like thinfilmmaterials.com, semiconductor manufacturers can safeguard their processes against contamination, downtime, and costly failures.
Invest in precision. Invest in purity. Choose TFM for your weldable fitting needs.