Gadolinium(III) Oxide Powder (Gd₂O₃)
Introduction
Gadolinium(III) Oxide Powder (Gd₂O₃) is a rare-earth compound widely used in electronics, optics, nuclear applications, and advanced ceramics. With its excellent magnetic, luminescent, and neutron-absorbing properties, Gd₂O₃ is considered a critical material in both research and industrial technologies.
Detailed Description
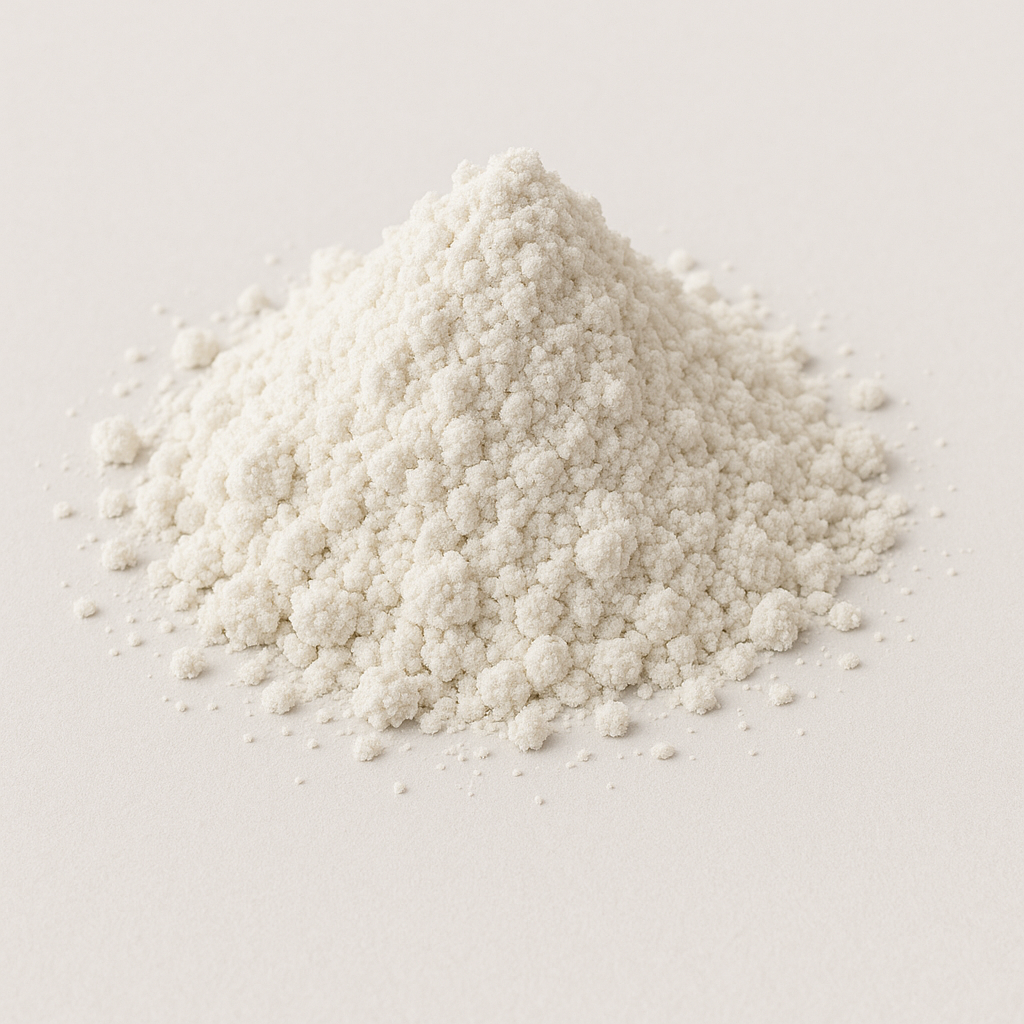
Gadolinium(III) Oxide is a white, odorless, stable powder with a high melting point (~2,420 °C) and density of ~7.41 g/cm³. It is commonly produced in high purity grades ranging from 99.9% (3N) to 99.999% (5N). The powder’s fine particle size ensures uniform sintering and high-density ceramics.
Key characteristics include:
Magnetic behavior: Gadolinium exhibits strong paramagnetism, making Gd₂O₃ essential in MRI contrast agent precursors and magneto-optical devices.
High neutron absorption cross-section: Used in nuclear reactor control materials.
Optical performance: Acts as a host material for rare-earth-doped phosphors and laser crystals.
Thermal stability: Suitable for high-temperature ceramics and coatings.
Applications
Gadolinium(III) Oxide Powder is applied in multiple industries, including:
Electronics: High-k dielectric thin films, capacitors, and memory devices.
Optics & Photonics: Phosphors, scintillators, and solid-state lasers.
Nuclear Technology: Absorber materials in reactor control rods.
Medical Imaging: Precursor for gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents.
Ceramics & Glass: Additive to improve refractive index and durability.
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% – 99.999% | Ensures optical clarity and magnetic reliability |
| Particle Size | 100 nm – 5 µm | Smaller particles improve sintering behavior |
| Appearance | White fine powder | Indicates high purity and stability |
| Melting Point | ~2,420 °C | High-temperature applications |
| Density | ~7.41 g/cm³ | Important for ceramics and nuclear materials |
Comparison with Related Materials
| Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Gadolinium Oxide (Gd₂O₃) | Magnetic & neutron absorption | Nuclear, MRI, optics |
| Yttrium Oxide (Y₂O₃) | High transparency & stability | Optical ceramics, coatings |
| Cerium Oxide (CeO₂) | Strong redox & polishing ability | Catalysts, glass polishing |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What purity levels are available? | 99.9% (3N), 99.99% (4N), and 99.999% (5N). |
| Can Gd₂O₃ be used in nuclear reactors? | Yes, due to its high neutron absorption properties. |
| Is it suitable for medical use? | Yes, as a precursor for MRI contrast agents, but requires further processing. |
| How is it packaged? | Vacuum-sealed in bottles or bags, larger quantities in export-grade drums. |
| Which industries benefit the most? | Electronics, optics, nuclear, medical imaging, and ceramics. |
Packaging
Gadolinium(III) Oxide Powder is packed in moisture-proof, airtight containers to preserve purity. For bulk orders, sealed drums or cartons with cushioning are used to prevent contamination and damage.
Conclusion
Gadolinium(III) Oxide Powder (Gd₂O₃) is a versatile rare-earth material essential for high-tech industries. Its magnetic, optical, and nuclear properties make it an irreplaceable component in electronics, photonics, medical, and energy applications.
For detailed specifications and a quotation, please contact us at [sales@thinfilmmaterials.com].




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.