Introduction
Lutetium Oxide (Lu₂O₃) Powder is a high-performance rare-earth oxide valued for its exceptional thermal stability, high density, and unique optical properties. As the heaviest and one of the most chemically stable rare-earth oxides, Lu₂O₃ is widely used in advanced ceramics, scintillation materials, laser hosts, and specialized electronic and optical research.
Detailed Description
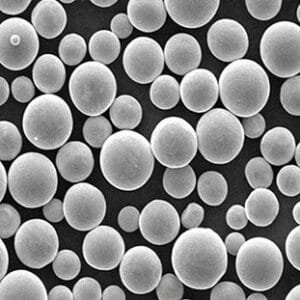
Lutetium oxide powder is produced through carefully controlled refining and calcination processes to achieve high chemical purity, uniform particle size distribution, and excellent phase consistency. These characteristics are critical for downstream processing such as sintering, crystal growth, and thin film fabrication.
Lu₂O₃ exhibits a very high melting point and strong resistance to chemical attack, making it suitable for high-temperature and harsh-environment applications. In optical and photonic fields, its high atomic number and density contribute to superior scintillation efficiency and optical performance. For ceramic processing, controlled powder morphology and purity directly influence densification behavior, grain growth, and final mechanical properties.
The powder can be supplied with tailored particle sizes and purity grades to meet the needs of research laboratories as well as industrial users.
Applications
Scintillator materials for medical imaging and radiation detection
Laser host materials and optical ceramics
Advanced structural and functional ceramics
Electronic materials and dielectric research
Thin film deposition research and compound synthesis
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Lu₂O₃ | Stable rare-earth oxide |
| Purity | 99.9% – 99.99% | Critical for optical & electronic performance |
| Appearance | White powder | Indicates high purity |
| Particle Size | Sub-micron to several microns (custom) | Affects sintering & processing |
| Melting Point | ~2490 °C | Enables high-temperature applications |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic | Stable phase for ceramics & optics |
Comparison with Related Rare-Earth Oxides
| Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Lutetium Oxide (Lu₂O₃) | High density, thermal stability | Scintillators & optics |
| Yttrium Oxide (Y₂O₃) | Cost-effective, versatile | Optical ceramics |
| Gadolinium Oxide (Gd₂O₃) | Magnetic properties | Imaging & electronics |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can purity and particle size be customized? | Yes, both purity grade and particle size can be tailored. |
| Is Lu₂O₃ suitable for ceramic sintering? | Yes, it is widely used in high-density ceramic processing. |
| Which industries use lutetium oxide most? | Medical imaging, optics, electronics, and advanced materials R&D. |
| How is the powder packaged? | Vacuum-sealed or moisture-protected packaging is used. |
| Is a Certificate of Analysis available? | Yes, CoA is provided upon request. |
Packaging
Our Lutetium Oxide Powder is carefully weighed, labeled, and sealed to prevent moisture uptake and contamination. Packaging options include vacuum-sealed bags or inert-atmosphere containers, with protective outer cartons suitable for international transport.
Conclusion
Lutetium Oxide Powder offers outstanding purity, thermal stability, and performance for demanding optical, ceramic, and electronic applications. With flexible specifications and reliable quality control, it is an excellent choice for both research and advanced industrial use.
For detailed specifications and a quotation, please contact us at sales@thinfilmmaterials.com.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.