Tellurium (Te) Powder
Overview
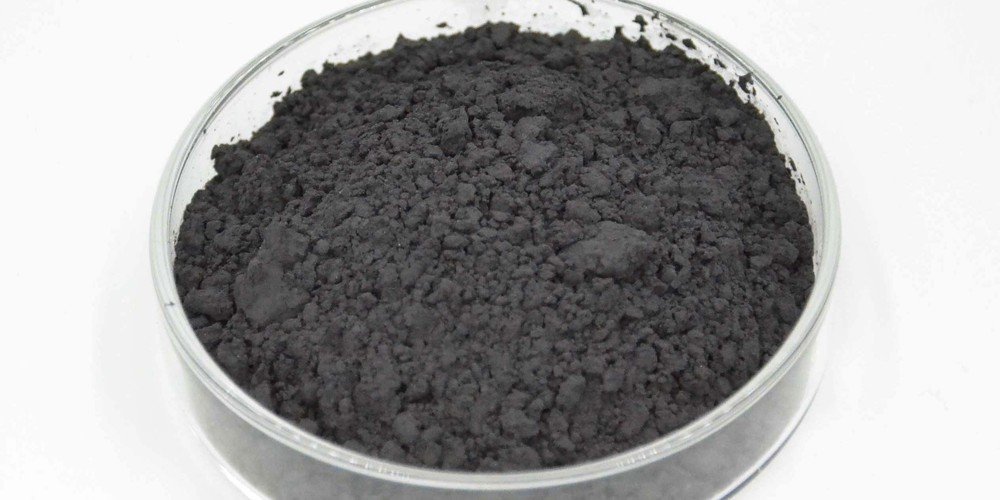
Tellurium (Te) powder is a high-purity metalloid material widely used in semiconductor, thermoelectric, and alloy applications. It exhibits semiconducting properties, good photoconductivity, and unique thermoelectric performance. With its crystalline structure and ability to form various compounds, tellurium is a critical material in infrared optics, phase-change memory, and photovoltaic devices.
Typical Applications
Tellurium powder is commonly utilized in:
Alloying with stainless steel and copper to improve machinability
Thermoelectric materials for power generation and cooling
Phase-change optical and memory devices
Infrared optical coatings
Semiconductor and photovoltaic research
Tellurium Powder Specification
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Te |
| Molecular Weight | 127.6 g/mol |
| Purity | 99.8% (3N), higher purities available |
| Appearance | Gray to silvery powder |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal |
| Melting Point | ~449.5 °C |
| Boiling Point | ~988 °C |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.5×10⁻³ Ω·m at 20 °C |
| Particle Size | 200 Mesh standard; other mesh sizes available |
| CAS Number | 13494-80-9 |
| Density | 6.24 g/cm³ |
Customized particle size distributions and purity levels are available upon request.
Applications of Tellurium Powder
Thermoelectric modules and devices
Semiconductor and photovoltaic thin films
Infrared optics and coatings
Alloying additive for improved metal machinability
Advanced material research and nanomaterials synthesis
Handling and Storage
Store in a cool, dry, and inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation
Avoid exposure to acids, moisture, and strong oxidizers
Use appropriate PPE to prevent inhalation of fine particles
Packaging
Tellurium powder is vacuum-sealed or packaged under inert gas in moisture-resistant containers. Each shipment is labeled with product name, purity, particle size, batch number, and net weight for full traceability and quality assurance.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.