Aluminium powder is a versatile and highly reactive material with a variety of industrial and commercial applications. This fine, metallic powder has unique properties that make it valuable in diverse sectors, from aerospace to medicine. As one of the most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust, aluminium is known for its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties, and electrical conductivity. When reduced to a fine powder, these properties become even more significant, offering a range of uses in different fields.
In this article, we will explore the various applications of aluminium powder, shedding light on its role in key industries such as manufacturing, energy production, and electronics. We will also look into some lesser-known uses of this powder, which contribute to advancements in science and technology.
The Basics of Aluminium Powder
Aluminium powder is produced through several methods, including atomization, ball milling, and electrolysis. The result is a fine powder with particles typically ranging from 5 to 500 micrometers in diameter. The powder can be either pure aluminium or alloyed with other metals, depending on its intended use.
Aluminium powder’s high surface area makes it highly reactive and an excellent candidate for various chemical reactions. The powder can burn at high temperatures, which makes it an essential component in the production of thermite, pyrotechnics, and other high-energy applications. Additionally, aluminium powder can act as a reducing agent in chemical reactions, providing a means to extract metals from their ores.
Key Applications of Aluminium Powder
1. Aerospace and Automotive Industries
One of the most significant applications of aluminium powder is in the aerospace and automotive industries, where it is used in a variety of components and processes. The aerospace industry, in particular, benefits from the lightweight and high-strength properties of aluminium, which are amplified when the material is in powder form.
In the manufacturing of aircraft, aluminium powder is often used in the production of lightweight composites. These composites help reduce the weight of aircraft, which in turn increases fuel efficiency and performance. Aluminium powder is also used in 3D printing technologies, where it allows for the creation of highly detailed and customized parts. This is especially useful for producing components with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to make using traditional manufacturing methods.
In the automotive industry, aluminium powder is used in the production of lightweight vehicles, contributing to better fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. Aluminium is also used in the manufacture of parts like engine components, chassis, and suspension systems, where its strength-to-weight ratio is essential for improving vehicle performance.
2. Pyrotechnics and Explosives
Aluminium powder is commonly used in pyrotechnics and explosives, primarily for its ability to produce bright, intense light and heat when burned. When combined with oxidizers such as potassium nitrate, aluminium powder creates highly exothermic reactions that are perfect for fireworks, flares, and other forms of pyrotechnic displays. The powder’s ability to burn at high temperatures makes it an essential ingredient in the production of thermite, a mixture of aluminium powder and iron oxide that produces intense heat capable of welding metals together.
In addition to pyrotechnics, aluminium powder is also utilized in explosives for both military and industrial applications. In these contexts, the powder serves as an energetic material that can amplify the power of explosions or accelerate chemical reactions. The small particle size of aluminium powder allows it to react more rapidly with other substances, making it ideal for use in explosives designed for demolition or mining operations.
3. Energy Production
Aluminium powder plays a significant role in energy production, particularly in the form of fuel. When mixed with other substances, aluminium powder can serve as a highly efficient fuel for thermochemical processes. In rocket propulsion, for instance, aluminium powder is often used in combination with other chemicals to create solid rocket propellants. These propellants are known for their high energy content and are used in both space exploration and military applications.
Another important energy-related use of aluminium powder is in the development of energy storage systems. Aluminium-air batteries, which utilize aluminium powder as an anode material, are being researched as a potential alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These batteries have a higher energy density, which could lead to longer-lasting and more efficient energy storage solutions for electric vehicles and other applications.
4. Metal Production and Metallurgy

In the metallurgical industry, aluminium powder is used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals from their ores. One of the most well-known applications of aluminium powder in metallurgy is in the production of titanium. Aluminium powder is used to reduce titanium tetrachloride (TiCl₄) into titanium metal, a process known as the Kroll process. The high reactivity of aluminium allows it to strip away the chlorine atoms from the titanium tetrachloride, leaving pure titanium behind.
Aluminium powder is also used in the production of other metals, such as uranium and chromium, as well as in the processing of ores to produce ferroalloys. The powder is effective in reducing metal oxides and enabling the extraction of valuable metals from their ores.
5. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
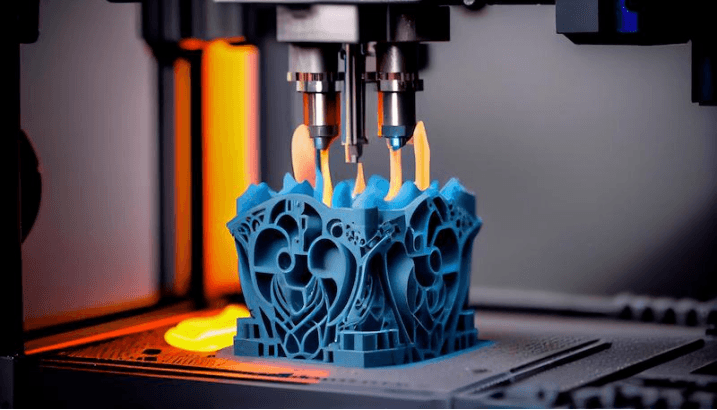
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, has revolutionized the way products are designed and produced. Aluminium powder is an essential material in certain 3D printing technologies, particularly selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM), where it is used to create complex, lightweight parts for a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
The use of aluminium powder in 3D printing allows manufacturers to create intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. The material’s ability to be precisely deposited in thin layers and fused together using high-energy lasers or electron beams makes it an ideal choice for creating parts with a high level of detail and accuracy.
6. Paints, Coatings, and Inks
Aluminium powder is also widely used in the production of paints, coatings, and inks. When mixed with other substances, aluminium powder creates a metallic finish that can be applied to a variety of surfaces. These coatings are used in a wide range of applications, from automotive and aerospace finishes to architectural coatings and industrial applications.
In paints and coatings, aluminium powder is often used to create a shiny, metallic effect. The powder reflects light, giving the surface a high-gloss appearance. Additionally, aluminium-based coatings are often used for their corrosion-resistant properties, helping to protect surfaces from environmental wear and tear.
Aluminium powder is also used in inks, particularly for printing on packaging materials. The powder helps create metallic ink formulations that provide a shiny, reflective finish, which is often used for decorative purposes or to create a premium look for high-end products.
7. Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Uses
In the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries, aluminium powder is sometimes used as an ingredient in various products. For example, it is used in the formulation of antacids, where its fine powder is combined with other substances to create a product that neutralizes stomach acid.
In cosmetics, aluminium powder is used in certain products like makeup, deodorants, and skin care formulations. Its reflective properties are utilized in products like highlighters and face powders, giving the skin a radiant or shimmering effect. The powder is also included in some deodorants, where it helps to control perspiration by absorbing moisture.
8. Chemical Reactions and Catalysis
Aluminium powder plays a crucial role as a catalyst and reactant in various chemical processes. Due to its high reactivity, it is often used in organic chemistry to reduce chemical compounds or to facilitate specific reactions. For example, aluminium powder is used in the production of certain chemicals by facilitating the reduction of organic compounds, such as halides, nitrates, and sulfonates.
The powder is also used in catalysis, particularly in reactions that require the presence of a solid material to accelerate a chemical transformation. Its fine particles provide a large surface area, making it an effective catalyst for many reactions.
Conclusion
Aluminium powder is a remarkably versatile material with applications spanning a wide range of industries, from aerospace to cosmetics. Its unique combination of lightweight, strength, and reactivity makes it indispensable in the production of lightweight components, energy-efficient fuels, and high-performance materials. As new technologies continue to emerge, the uses of aluminium powder are expected to expand, creating even more opportunities for innovation across various fields.
From pyrotechnics and explosives to 3D printing and energy storage, aluminium powder plays an essential role in driving progress in science and technology. Whether as a fuel in rocket propulsion systems or as a catalyst in chemical reactions, aluminium powder’s significance in modern industrial applications cannot be overstated. As industries continue to evolve and demand more advanced materials, aluminium powder will remain a key player in shaping the future of technology and innovation.