Introduction
Potassium Bromide (KBr) is one of the most widely used optical materials for infrared research, spectroscopy, and thin film applications. As a crystalline alkali halide compound, KBr offers exceptional transmission across a broad infrared spectrum, very low optical absorption, and a chemically stable lattice structure that makes it suitable for high-precision scientific and industrial environments.
Within the thin film community, KBr provides a dependable substrate for evaporation, organic film deposition, cryogenic studies, and infrared optical system development. Thin Film Materials (TFM) supplies KBr substrates manufactured with laboratory-grade precision, excellent flatness, and superior surface quality, ensuring reproducible performance for advanced applications.
Material Properties of Potassium Bromide (KBr)
Optical Transmission Range
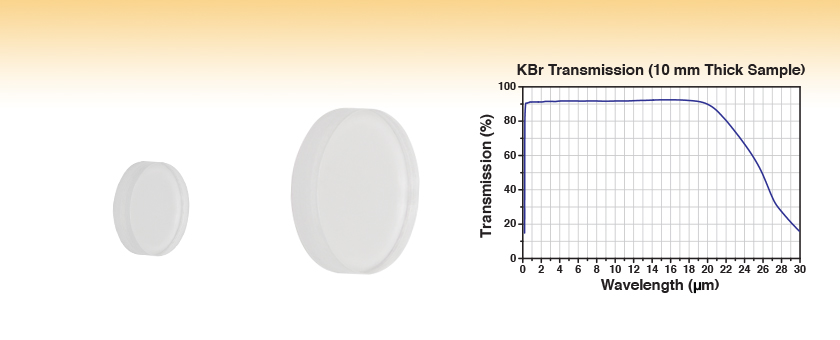
KBr offers outstanding transparency from 0.2 μm to 25–30 μm, covering the near-IR, mid-IR, far-IR, and part of the UV spectrum. This rare transmission range is one of the primary reasons KBr remains indispensable for IR-related research and instrumentation.
Chemical Inertness
KBr is chemically stable in the presence of oils, many organic solvents, and most weak acids and bases. While hygroscopic, its crystal structure remains stable under controlled humidity conditions, making it ideal for sealed or dry environments.
Low Background Signal
KBr’s minimal IR absorption ensures extremely low spectral background noise, essential for sensitive spectroscopic measurements, thin film analysis, and molecular vibration studies.
Surface Quality and Fabrication
KBr can be polished into high-accuracy windows, plates, circular substrates, and custom wafers. Its machinability allows fabrication into optical-grade surfaces suitable for infrared imaging, sensing, and thin film deposition.
Applications in Infrared Spectroscopy
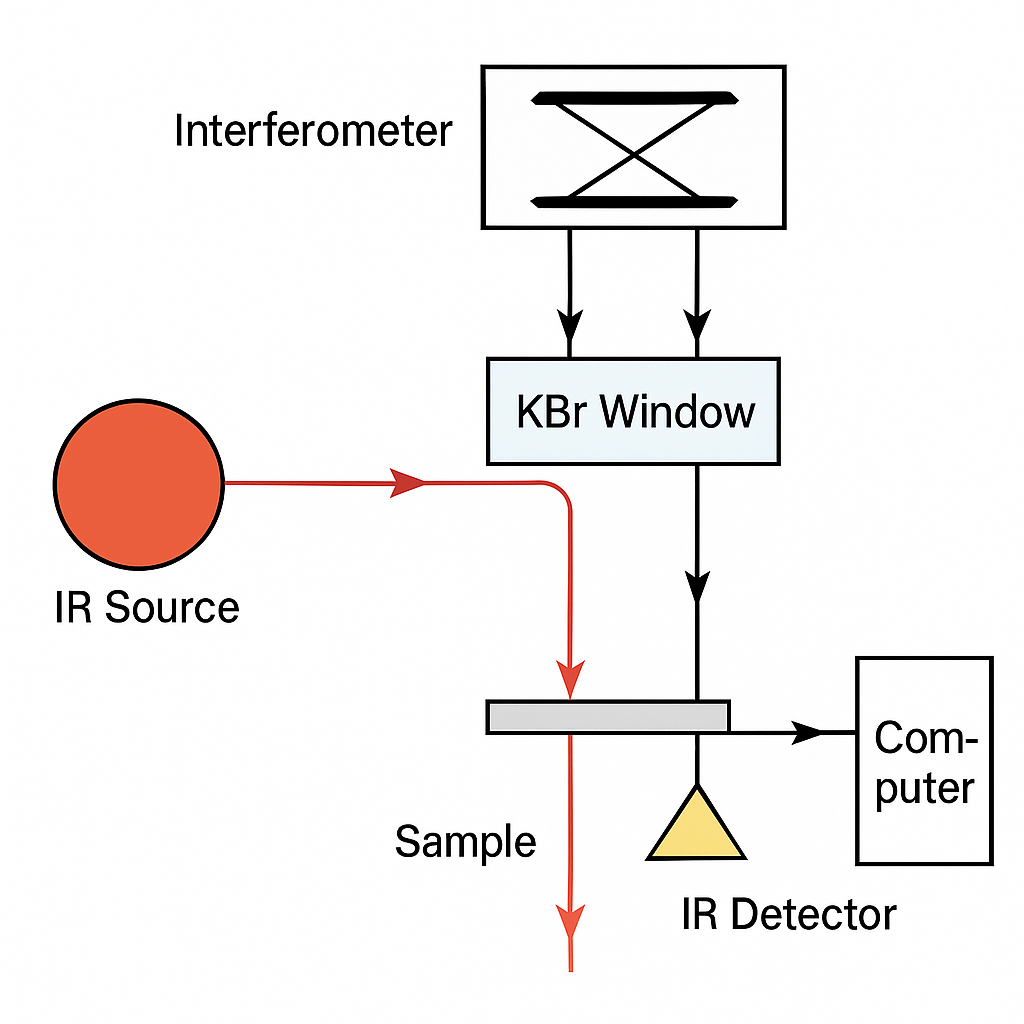
FTIR Spectroscopy
KBr plays a fundamental role in FTIR as:
- Sample windows
- Transmission substrates
- Beamline optical elements
- Carriers for pressed-pellet preparations
It supports a broad range of analytical tasks such as:
- Functional group identification in organic chemistry
- Polymer and elastomer characterization
- Pharmaceutical ingredient verification
- Environmental contaminant detection
- Fuel and lubricant analysis
KBr Pellets for Solid Sample Preparation
Ground KBr mixed with samples and pressed into transparent pellets is a standard FTIR method. Industries relying on this technique include pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, plastics, forensics, and environmental labs.
IR Windows in Spectrometer Beam Paths
KBr windows are used for:
- Reaction chamber monitoring
- Gas-phase analysis
- Sealed optical cells
- Infrared imaging calibration
Their low interference ensures high-fidelity IR measurements.
KBr Substrates in Thin Film Research and Deposition
Thin Film Absorption and Transmission Studies
KBr’s near-ideal IR baseline enables:
- Study of IR-active phonon modes
- Analysis of organic and polymer thin films
- Semiconductor absorption behavior
- Nanomaterial optical characterizations
Organic Films and Low-Temperature Deposition
KBr substrates support:
- Molecular beam epitaxy of organic materials
- Cryogenic thin film growth
- Deposition of biomolecules
- Polymer coating analysis
Its chemical neutrality ensures that deposited films exhibit undistorted spectral features.
Vacuum Evaporation and PVD
KBr is widely used in:
- Thermal evaporation
- Low-temperature physical vapor deposition
- Laser-assisted thin film formation
A unique advantage is that deposited films can be lifted off by dissolving KBr in water, allowing researchers to transfer films to other substrates for further testing.
Quantum Materials and 2D Materials
KBr supports emerging research in:
- Van der Waals materials
- Terahertz and phonon-based materials
- Excitonic and IR quantum materials
- 2D thin film systems
Its broad IR transparency allows direct study of low-energy excitations.
Applications in Biomedical and Life Sciences
FTIR-Based Pathology and Diagnostics
KBr is used in:
- Cell and tissue IR analysis
- Serum and biofluid fingerprinting
- Disease marker detection
- Molecular structural studies
FTIR-based diagnostics increasingly rely on KBr substrates due to their stability and spectral clarity.
Infrared Biosensors
KBr substrates support biosensor development involving:
- Proteins and enzymes
- Viral and bacterial components
- Biomolecule interactions
- Bio-surface adsorption studies
Pharmaceutical Characterization
Pharmaceutical research uses KBr for:
- Studying polymorphs
- Identifying APIs
- Investigating excipient interactions
- Monitoring solid-state transitions
Industrial and Manufacturing Applications
Polymer and Plastic Manufacturing
KBr enables IR characterization of:
- Polymeric films
- Elastomers
- Additives and fillers
- Coatings and packaging materials
Petrochemical Analysis
KBr substrates are widely used for:
- Lubricants and engine oils
- Fuels and combustion byproducts
- Chemical feedstocks
- Process control monitoring
Environmental and Air Quality Testing
KBr supports environmental IR analysis for:
- Particulate matter
- Airborne pollutants
- Greenhouse gases
- Combustion aerosols
Optical and Instrument Manufacturing
Infrared Instrument Components
KBr is used in:
- IR spectrometer optics
- Beam splitters
- Calibration windows
- Protective IR barriers
- Flow-cell assemblies
Infrared Imaging and Sensing
KBr’s broad transmission makes it ideal for specialized IR imaging, thermal sensing, and metrology systems.
Emerging and Specialized Applications
Mid-IR and Tunable Laser Optics
KBr is compatible with:
- Mid-infrared tunable lasers
- Quantum cascade lasers
- IR nonlinear optics
Terahertz Research
KBr exhibits useful transmission into the THz region, enabling:
- Terahertz spectroscopy
- Low-frequency phonon research
- IR-to-THz hybrid systems
Surface Science and Electrochemistry
KBr provides an optically transparent base for:
- Adsorbed molecular layers
- Chemical reaction monitoring
- Modified thin film surfaces
Storage, Handling, and Operational Considerations
Moisture Sensitivity
KBr is hygroscopic and requires:
- Dry nitrogen cabinets
- Vacuum-sealed packaging
- Low-humidity environments
Handling Methods
Operators should use:
- Gloves
- Dry tweezers
- Clean dry workstations
Cleaning Guidelines
KBr must not be cleaned with water. Only anhydrous solvents are suitable.
Why KBr Substrates Remain Indispensable
KBr continues to outperform alternatives due to:
- Exceptional infrared transparency
- Minimal spectral interference
- Broad compatibility with organic, inorganic, and biological materials
- Transferable thin film deposition capability
- High-accuracy surface finishing
- Reliability across spectroscopy and thin film research
While CaF₂, BaF₂, ZnSe, and Ge have their advantages, KBr remains the first choice for FTIR and IR-intensive applications.
Conclusion
Potassium Bromide (KBr) Substrates play a foundational role in spectroscopy, thin-film research, biomedical diagnostics, environmental analysis, petrochemical testing, polymer science, and optical instrumentation. With unmatched IR transparency and minimal background interference, KBr continues to enable precise and high-quality scientific analysis.
TFM provides precision-polished KBr substrates suitable for R&D laboratories, advanced manufacturing, and specialized optical systems. For specifications or custom sizes, please contact:
Related Products
Potassium Bromide Substrate (KBr)



