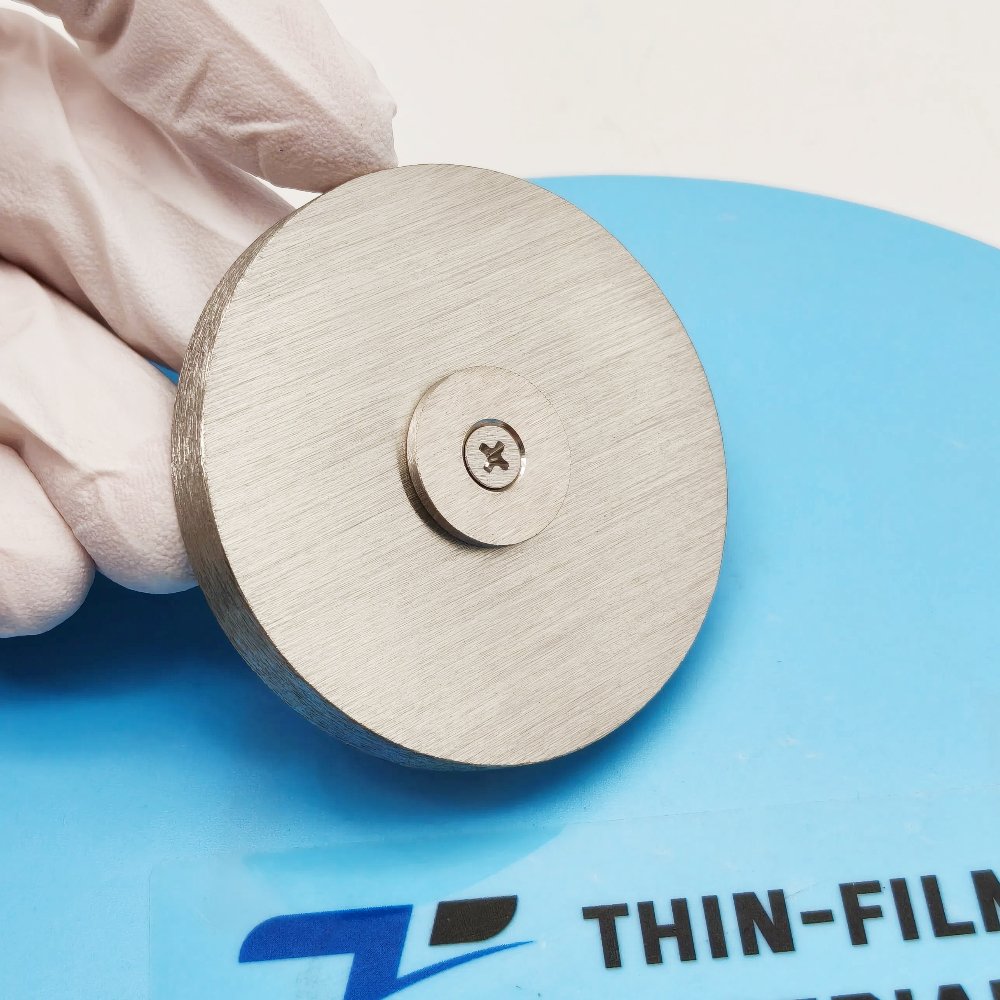
Scandium Sputtering Target
The Scandium Sputtering Target is a high-purity metallic material widely used in thin film deposition technologies such as PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and magnetron sputtering. As a rare and lightweight transition metal, scandium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, low density, and high melting point, making it ideal for advanced applications in semiconductors, optics, and high-strength alloys.
Detailed Description
Scandium (Sc) is a silvery-white, soft metal with outstanding chemical stability and a melting point of 1541 °C. It forms uniform, adherent films that are useful for both functional and structural coatings. Scandium sputtering targets are typically produced by vacuum melting or hot-press sintering to achieve high density and purity, ensuring excellent film quality and repeatable deposition rates.
Key Features:
High purity (up to 99.99%) minimizes contamination and improves electrical and optical properties.
Excellent uniformity for consistent film deposition.
High thermal and chemical stability enables use in demanding process environments.
Customizable shapes and bonding options for different sputtering systems.
Applications
Scandium sputtering targets are used in:
Semiconductor thin films – for developing advanced device layers and interconnects.
Optoelectronic coatings – transparent conductive and anti-reflective films.
Alloy deposition – improving mechanical strength and corrosion resistance of aluminum and other alloys.
Solid-state lighting – in LED and phosphor thin film production.
Aerospace and energy industries – as part of Sc–Al alloys and coating systems for lightweight components.
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% – 99.99% (3N–4N) | High purity ensures consistent film properties |
| Density | ≥ 99% theoretical | Reduces voids and improves sputtering efficiency |
| Diameter | 25 – 200 mm (custom) | Fits most sputtering systems |
| Thickness | 3 – 6 mm | Balances lifetime and sputtering uniformity |
| Backing Plate | Copper / Titanium | Improves heat transfer and bonding strength |
Comparison with Related Materials
| Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Scandium (Sc) | Enhances optical & electrical film performance | Semiconductor & LED |
| Yttrium (Y) | High transparency & hardness | Optical coatings |
| Aluminum (Al) | Cost-effective, lightweight | Conductive coatings |
| Scandium Oxide (Sc₂O₃) | High ionic conductivity | SOFC & optical films |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can Scandium targets be customized? | Yes, size, purity, and bonding can be customized. |
| What purity levels are available? | Typically 3N (99.9%) and 4N (99.99%). |
| What bonding materials are used? | Copper or titanium plates for thermal management. |
| How is it packaged? | Vacuum-sealed with foam and export-safe cartons or wooden crates. |
| Which industries use it most? | Semiconductors, LEDs, optics, aerospace, and R&D. |
Packaging
Each Scandium Sputtering Target is precisely labeled and vacuum-sealed in cleanroom conditions to prevent oxidation and contamination. Foam padding and sturdy cartons or wooden crates ensure damage-free transport.
Conclusion
Scandium sputtering targets deliver exceptional performance for high-end thin film deposition, offering purity, stability, and customization. Their unique properties make them essential in advanced electronics, optics, and aerospace coating technologies.
For detailed specifications and pricing, please contact us at [sales@thinfilmmaterials.com].





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.