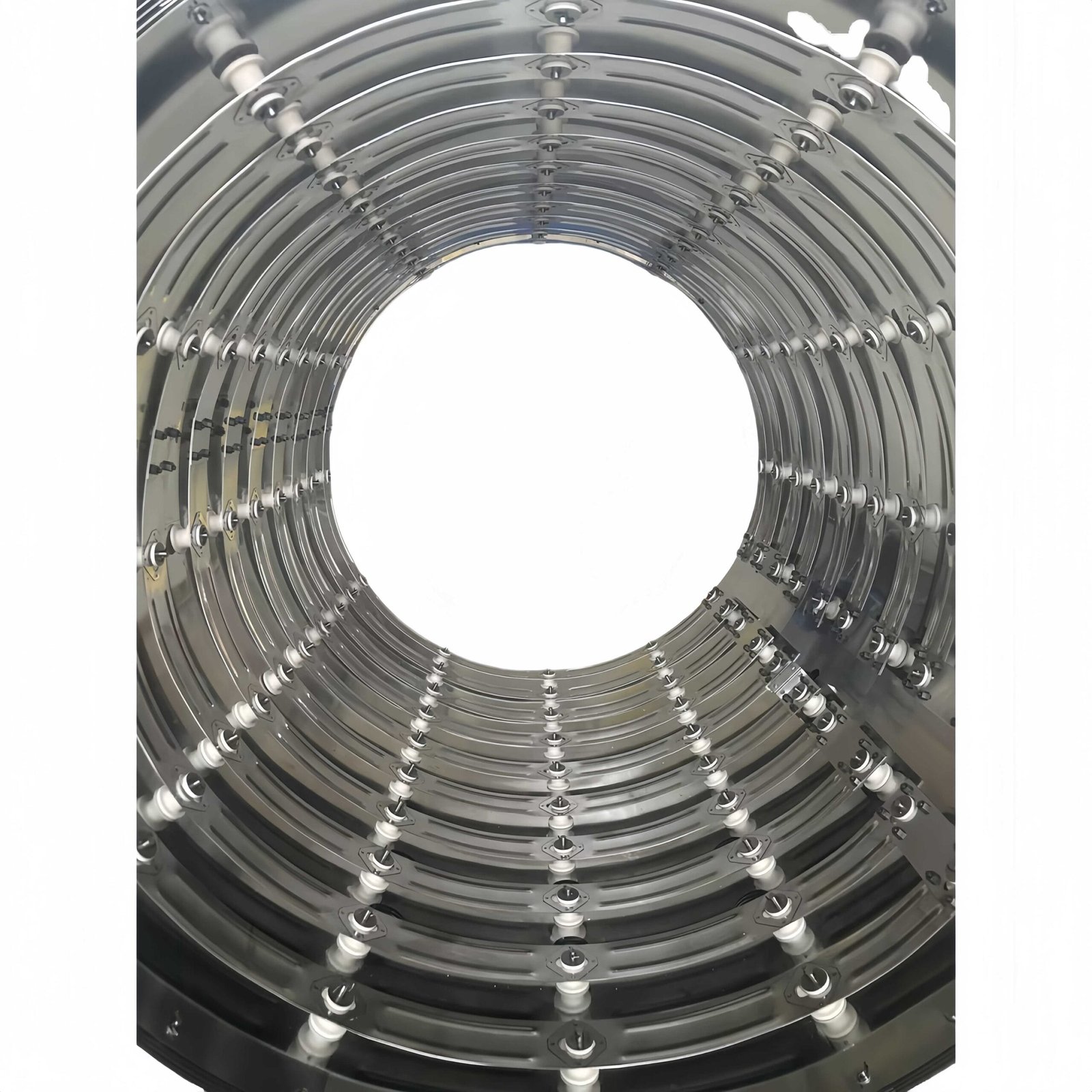
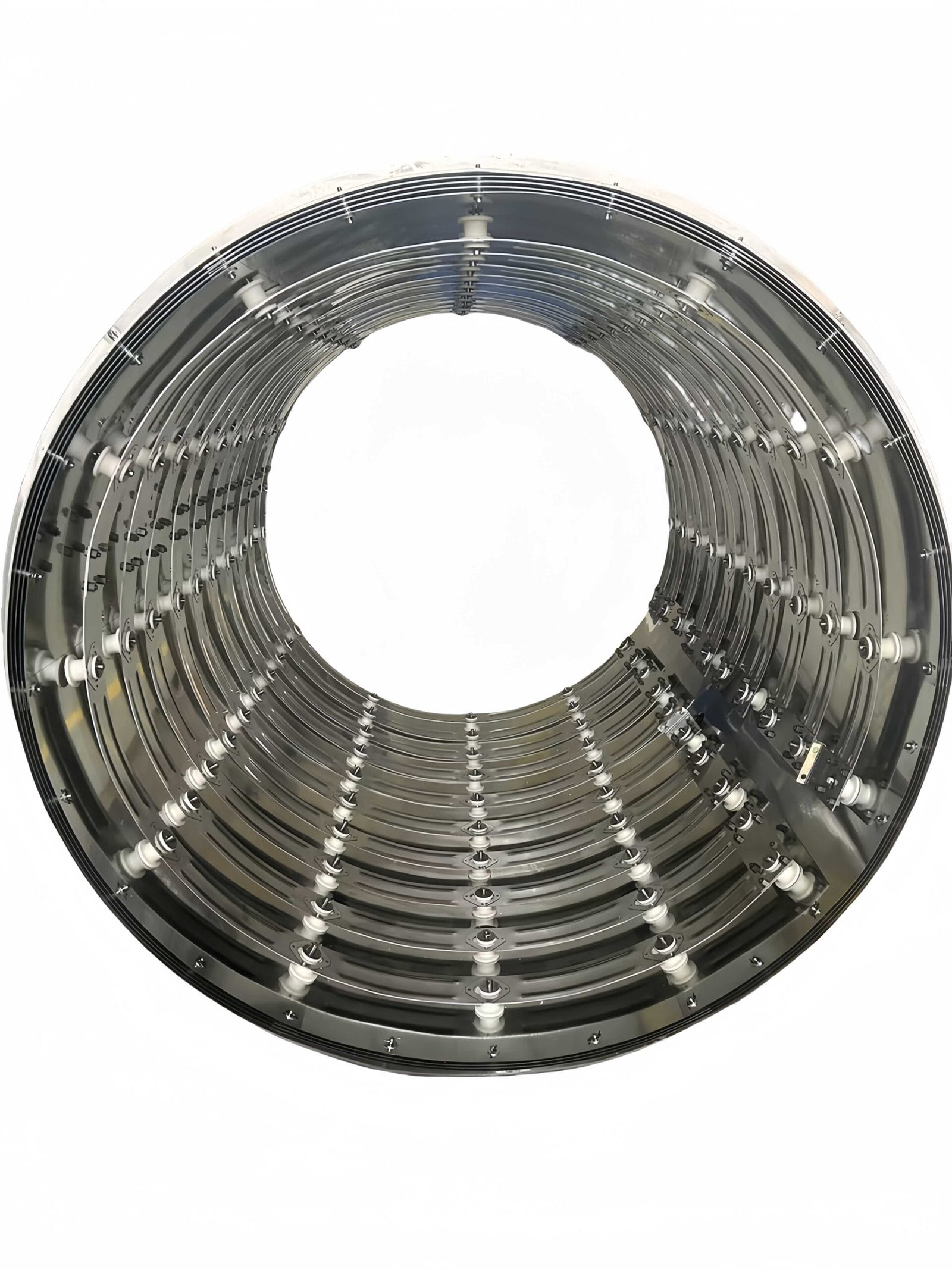
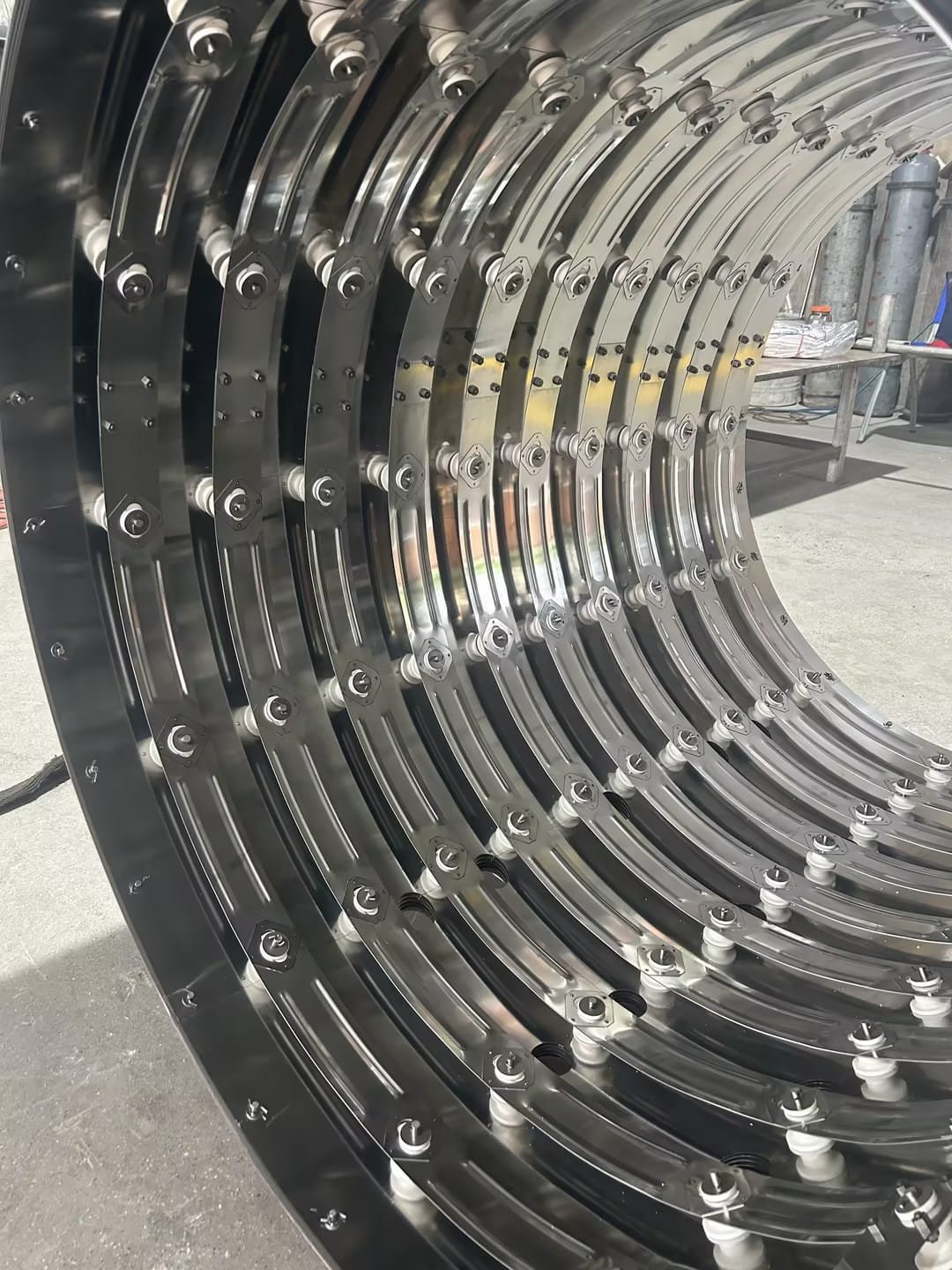
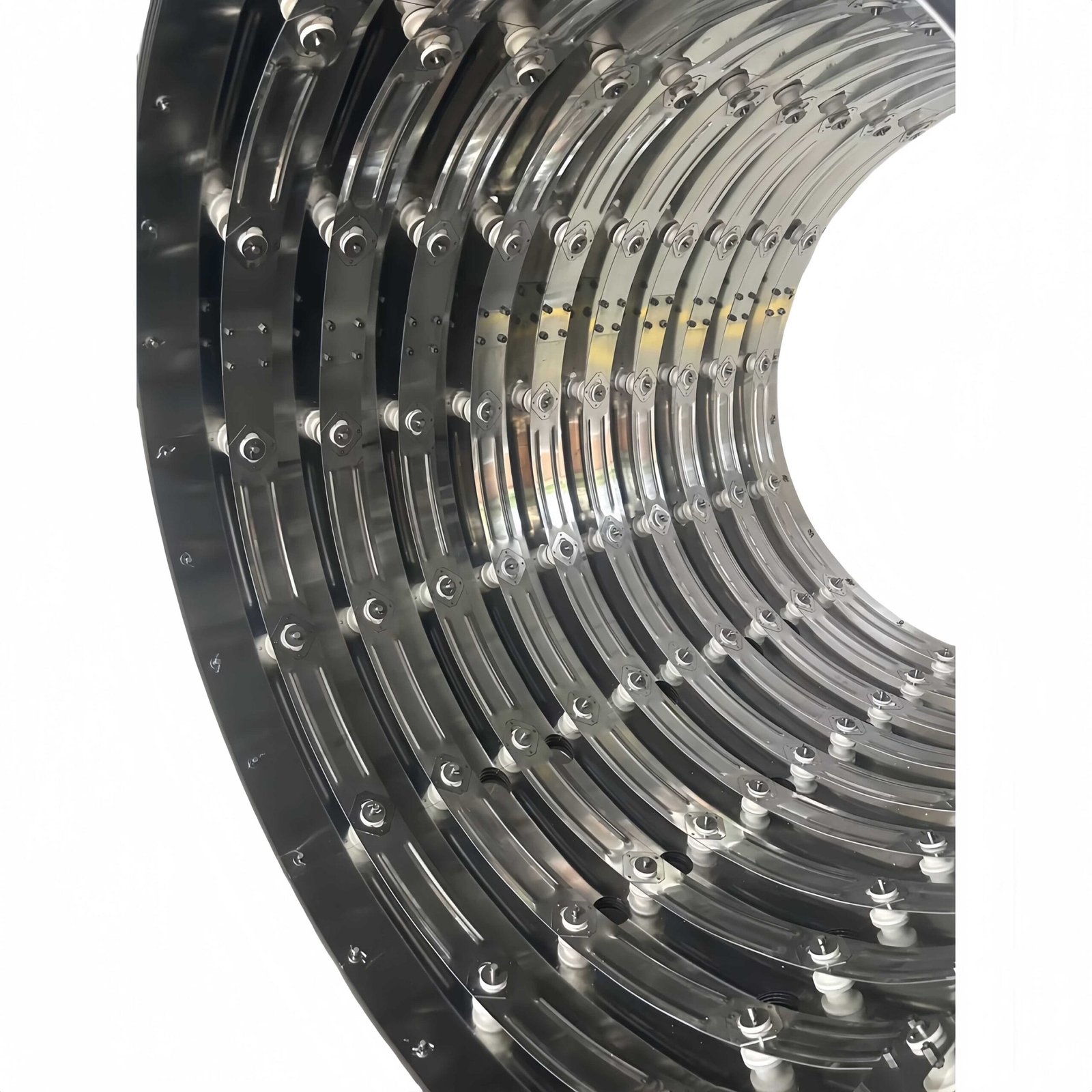
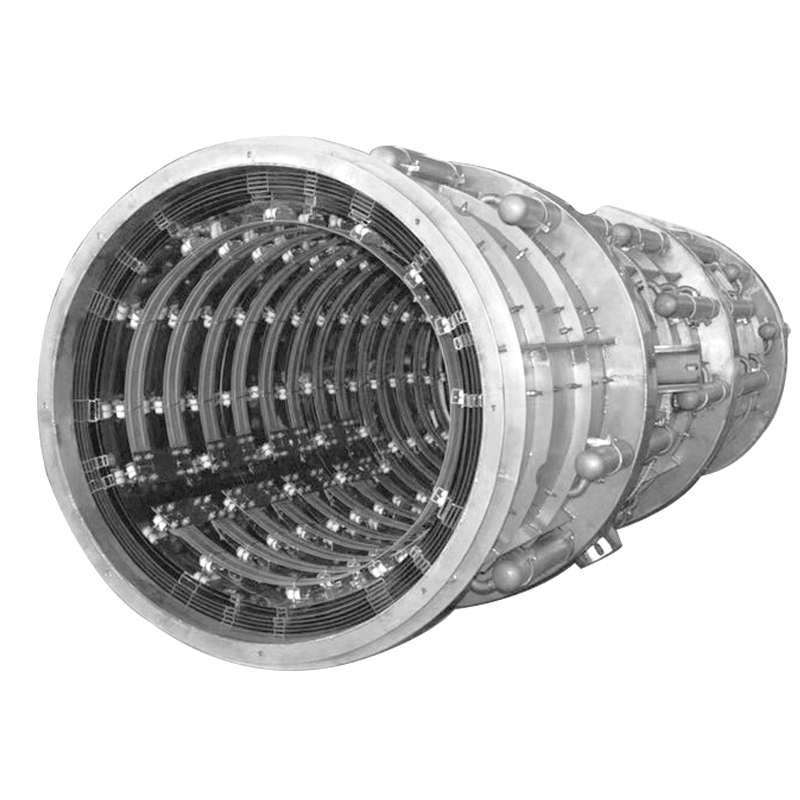
Detailed Overview of Vacuum Furnace Chambers
1. Function of the Furnace Chamber
The vacuum furnace chamber plays a pivotal role in the heat treatment process by:
- Stabilizing the Workpiece: It keeps the workpiece securely positioned throughout the heat treatment cycle.
- Protecting the Workpiece: The chamber shields the workpiece from external threats like oxidation, carburization, and sulfuration, preserving material integrity and enabling precise thermal processing.
2. Essential Characteristics of the Furnace Chamber
Operating in a vacuum environment requires the chamber to meet several critical criteria:
- High-Temperature Resistance: The chamber materials must withstand extreme heat without deforming or deteriorating under intense thermal stress.
- Vacuum Integrity: The chamber must maintain airtightness to prevent gas leaks and ensure an optimal vacuum environment throughout the process.
- Corrosion Resistance: Given that some vacuum conditions may involve corrosive atmospheres, the chamber materials must exhibit high resistance to corrosion to ensure durability and performance.
3. Maintenance Requirements for the Furnace Chamber
To guarantee reliable long-term operation, regular maintenance of the vacuum furnace chamber is essential:
- Seal Integrity Inspection: Regularly inspect the chamber’s seals to prevent gas leakage, which could compromise the vacuum environment.
- Routine Cleaning: Periodic cleaning is required to remove debris or residues affecting performance and heat transfer efficiency.
- Condition Monitoring: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or structural damage and address any issues promptly through repair or replacement to prevent operational failures.
4. Cleaning Procedures for the Furnace Chamber
Proper cleaning should be conducted after the chamber fully cools to room temperature. Cleaning methods include:
- Mechanical Cleaning: Physically removing debris or build-up using tools.
- Chemical Cleaning: Using appropriate chemicals to dissolve and remove contaminants.
- Electrolytic Cleaning: Applying an electrolytic process to clean stubborn residues. The choice of cleaning method depends on the nature and severity of contamination.
5. Materials Used in Vacuum Furnace Chambers
Vacuum furnace chambers are generally constructed from materials like stainless steel, known for their:
- High-Temperature Tolerance: Capable of maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat.
- Corrosion Resistance: Providing protection against corrosive elements in specific vacuum environments.
- Mechanical Strength and Chemical Stability: Ensuring the chamber remains durable and reliable during repeated high-temperature operations.
The vacuum furnace chamber is a crucial element in ensuring optimal heating efficiency and workpiece quality. Its performance, combined with proper maintenance, directly influences the overall success of the heat treatment process. Selecting materials with the appropriate thermal and chemical resistance, along with consistent maintenance, will ensure long-lasting, stable operation of the vacuum furnace system.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.