Introduction
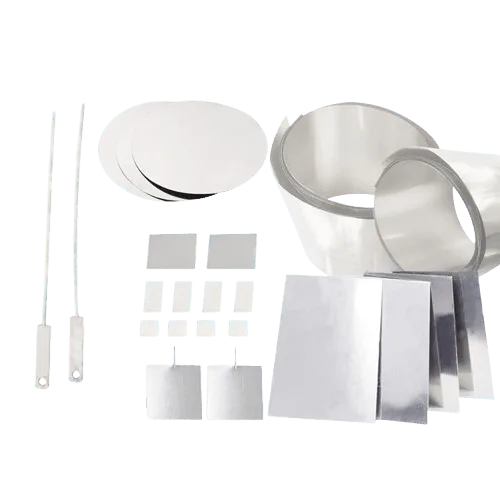
Platinum sheet and platinum foil are among the most technically significant forms of noble metal materials used in advanced scientific research and high-end industrial manufacturing. Owing to platinum’s unique combination of chemical inertness, thermal stability, electrical reliability, and outstanding mechanical workability, platinum sheet and foil are widely adopted in environments where performance margins are extremely narrow and material failure is unacceptable.
Unlike bulk platinum components, sheet and foil forms provide a large functional surface area, precise thickness control, and flexible integration into complex systems. These characteristics make platinum sheet and foil indispensable in laboratories, semiconductor fabrication, chemical processing, energy systems, medical technology, and optical manufacturing.
This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the major application scenarios of platinum sheet and foil, focusing on why these forms are selected, how their intrinsic properties support each application, and what technical advantages they offer over alternative materials.
Fundamental Properties Supporting Platinum Sheet & Foil Applications
Before examining specific application fields, it is essential to understand the material characteristics that define platinum sheet and foil performance.
Exceptional Chemical Stability
Platinum is one of the most chemically inert metals known. It resists:
Oxidation at elevated temperatures
Attack by strong acids and bases
Corrosion in halogenated and sulfur-containing atmospheres
This stability ensures that platinum sheet and foil do not introduce contamination or degradation products during long-term exposure to aggressive chemical environments.
With a melting point of approximately 1768 °C, platinum maintains structural integrity and functional performance at temperatures that exceed the limits of most engineering metals. Platinum foil and sheet remain stable under continuous thermal cycling, making them suitable for both steady-state and transient high-temperature operations.
Stable Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Platinum exhibits predictable electrical resistivity and a well-defined temperature coefficient, enabling accurate and repeatable electrical performance. Its thermal conductivity supports uniform heat distribution, critical in heating, sensing, and energy applications.
Excellent Ductility and Processability
Platinum can be rolled into extremely thin foils while maintaining mechanical coherence. Platinum sheet and foil can be cut, stamped, welded, and formed without cracking, enabling precise customization for specialized designs.
Applications in Scientific Research and Laboratory Systems
High-Temperature Experimental Substrates
In materials science, chemistry, and physics laboratories, platinum foil is frequently used as:
- A substrate for high-temperature reactions
- A support material for catalysts and powders
- A containment layer for samples under reactive atmospheres
Because platinum does not react with most substances, it allows researchers to isolate experimental variables and obtain reproducible results without interference from container materials.
Reference and Calibration Components
Platinum sheet is often employed as a reference material in:
- Thermal analysis instruments
- Precision resistance measurements
- Long-term calibration systems
Its dimensional and electrical stability ensures minimal drift over time, which is essential for accurate scientific measurement.
Corrosive and Reactive Media Experiments
Laboratory experiments involving aggressive chemicals or high-purity gases rely on platinum foil for:
- Acid vapor exposure
- Oxidation and reduction studies
- Controlled atmosphere testing
In these environments, platinum outperforms stainless steels, nickel alloys, and ceramic alternatives in terms of durability and purity.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing Applications
Electrode and Contact Materials
Platinum sheet and foil are widely used as electrodes in:
- Power electronics
- Sensors and detectors
- High-temperature electronic devices
Their resistance to diffusion and electromigration under elevated temperatures ensures stable electrical interfaces throughout device lifetimes.
Thin-Film Processing and Deposition Support
In semiconductor fabrication, platinum foil serves as:
- Masking material during deposition
- Structural support in high-temperature processes
- Conductive components in vacuum systems
Platinum’s low vapor pressure minimizes contamination risks in ultra-clean manufacturing environments.
MEMS and Micro-Device Integration
Platinum foil is especially valuable in MEMS and micro-heater designs due to:
- Consistent resistive heating behavior
- Compatibility with micro-fabrication processes
- Long-term reliability under cyclic electrical loading
Chemical Processing and Catalytic Applications

Catalytic Reaction Surfaces
Platinum is inherently catalytic, and platinum sheet provides:
- A large, stable catalytic surface
- Uniform reaction zones
- Structural support for catalyst coatings
These features make platinum sheet and foil ideal for gas-phase reactions and high-temperature catalytic studies.
Corrosion-Resistant Chemical Equipment
In chemical plants handling nitric acid, sulfuric acid, chlorine compounds, or mixed corrosive streams, platinum sheet is used for:
- Reactor linings
- Electrodes
- Heat transfer elements
The extended service life of platinum often offsets its initial material cost.
Electrochemical Systems
Platinum foil functions as a standard electrode material in:
- Electrolysis cells
- Analytical electrochemistry
- Research-scale energy conversion systems
Its electrochemical stability ensures accurate reaction control and repeatable performance.
Energy and High-Temperature Engineering Applications
Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Technologies
Platinum sheet and foil are used in:
- Fuel cell electrodes
- Current collectors
- Structural supports in hydrogen systems
Their resistance to oxidation and hydrogen embrittlement is essential for long-term reliability.
Heating Elements and Thermal Control
Platinum sheet is employed in:
- Precision heating elements
- High-temperature furnaces
- Controlled thermal zones
Its predictable resistance allows accurate temperature control over extended operation periods.
Temperature Measurement Systems
Platinum foil forms the basis of many high-precision temperature sensors due to:
- Linear resistance-temperature behavior
- Long-term calibration stability
- High operating temperature limits
Medical and Biomedical Applications
Implantable and Diagnostic Devices
Platinum’s excellent biocompatibility makes platinum sheet and foil suitable for:
- Neural stimulation electrodes
- Implantable sensors
- Long-term diagnostic components
The material does not corrode or release harmful ions in biological environments.
Medical Research Equipment
In laboratory and clinical research, platinum foil is used in:
- Sterilizable high-temperature components
- Chemically inert analytical tools
- Precision instrumentation
Glass, Optical, and Advanced Manufacturing Applications
Glass Melting and Crystal Growth
Platinum sheet is widely used in:
- High-purity glass melting systems
- Optical crystal growth equipment
- Molten material handling components
Its non-reactive nature ensures that optical materials remain uncontaminated.
Precision Optical and Structural Components
In advanced optical manufacturing, platinum sheet provides:
- Dimensional stability
- Thermal uniformity
- Long-term reliability in demanding environments
Conclusion
Platinum sheet and platinum foil represent a class of materials defined by extreme reliability, chemical neutrality, and thermal endurance. Their application across scientific research, electronics, chemical processing, energy systems, medical technology, and optical manufacturing reflects a consistent demand for materials that perform predictably under the most challenging conditions.
While platinum is a premium material, its long service life, minimal maintenance requirements, and unparalleled stability often result in lower total cost of ownership for critical applications. As advanced technologies continue to push operational boundaries, platinum sheet and foil will remain essential materials for environments where performance cannot be compromised.