Introduction
Lanthanum Strontium Manganate sputtering targets, commonly referred to as LSMO (La₁₋ₓSrₓMnO₃), are widely used functional oxide materials in advanced thin-film deposition. Thanks to their unique combination of electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, and chemical stability, LSMO targets are essential for fabricating complex oxide thin films used in spintronics, magnetic devices, and oxide electronics research.
Detailed Description
Lanthanum Strontium Manganate is a perovskite-structured mixed-valence manganese oxide. Partial substitution of lanthanum by strontium precisely tunes the Mn³⁺/Mn⁴⁺ ratio, enabling controllable electrical and magnetic behavior. This tunability is one of the key reasons LSMO has become a benchmark material in correlated electron systems and oxide heterostructure studies.
Our Lanthanum Strontium Manganate sputtering targets are produced from high-purity raw materials using optimized solid-state reaction and sintering processes. The resulting targets exhibit high density, compositional uniformity, and stable sputtering behavior under RF or pulsed-DC conditions. Careful control of stoichiometry ensures reproducible film properties, which is critical for epitaxial growth and device-grade thin films.
LSMO targets are available in planar disc formats as well as customized shapes. Bonding options such as indium bonding or elastomer bonding to copper backing plates can be provided to improve thermal management and target integrity during high-power sputtering. These targets are compatible with a wide range of sputtering systems used in both research laboratories and pilot-scale production.
Applications
Lanthanum Strontium Manganate sputtering targets are primarily used in the deposition of functional oxide thin films for:
Spintronic devices and magnetic tunnel junctions
Oxide electronics and correlated electron systems
Electrodes for ferroelectric and multiferroic thin films
Magnetoresistive sensors and memory devices
Epitaxial oxide heterostructures grown by sputtering
Academic and industrial R&D on perovskite oxides
Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | La₁₋ₓSrₓMnO₃ (LSMO) | Determines electrical & magnetic properties |
| Purity | 99.9% – 99.99% | Reduces impurities affecting film performance |
| Sr Doping (x) | 0.1 – 0.4 (custom) | Tunes conductivity and magnetism |
| Diameter | 1″ – 4″ (custom available) | Fits standard sputtering cathodes |
| Thickness | 3 – 6 mm | Influences sputtering lifetime |
| Density | ≥ 95% of theoretical | Ensures stable sputtering rate |
| Backing Plate | Optional Cu / Al | Improves heat dissipation |
Comparison with Related Materials
| Material | Key Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Lanthanum Strontium Manganate (LSMO) | Conductive, ferromagnetic oxide | Spintronics, oxide electronics |
| Lanthanum Manganate (LaMnO₃) | Antiferromagnetic, insulating | Fundamental oxide research |
| Strontium Ruthenate (SrRuO₃) | Metallic oxide electrode | Ferroelectric electrodes |
| Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) | Transparent conductor | Displays, optoelectronics |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can the Sr doping level be customized? | Yes, the La/Sr ratio can be tailored to application requirements. |
| Are these targets suitable for RF sputtering? | Yes, they are compatible with RF and pulsed-DC sputtering. |
| Do you offer bonded targets? | Yes, indium-bonded or elastomer-bonded options are available. |
| What density can be achieved? | Typical density exceeds 95% of theoretical density. |
Packaging
Our Lanthanum Strontium Manganate Sputtering Targets are individually labeled for traceability and quality assurance. Each target is vacuum-sealed and cushioned with protective materials to prevent contamination or mechanical damage during storage and transportation, ensuring they arrive ready for immediate installation.
Conclusion
Lanthanum Strontium Manganate sputtering targets provide a reliable and high-performance solution for depositing complex oxide thin films with well-defined electrical and magnetic properties. With controlled stoichiometry, high density, and flexible customization options, these targets are well suited for advanced research and specialized device fabrication.
For detailed specifications and a quotation, please contact us at sales@thinfilmmaterials.com.
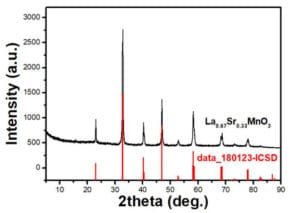
XRD Chart of Lanthanum Strontium Manganate Sputtering Targets





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.