Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target Description
Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target is a mixed oxide ceramic sputtering target, typically produced through high-temperature sintering or recrystallization of an oxide mixture of lithium and iron. Lithium iron phosphate appears as a gray, red-grey, brown, or black solid that is insoluble in water. It possesses unique physical properties, making it ideal for specialized applications in the electronics, superconductivity, and optical industries.
Related Products: Lithium Sputtering Targets, Platinum Sputtering Targets.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target Specification
| Material Type | Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target |
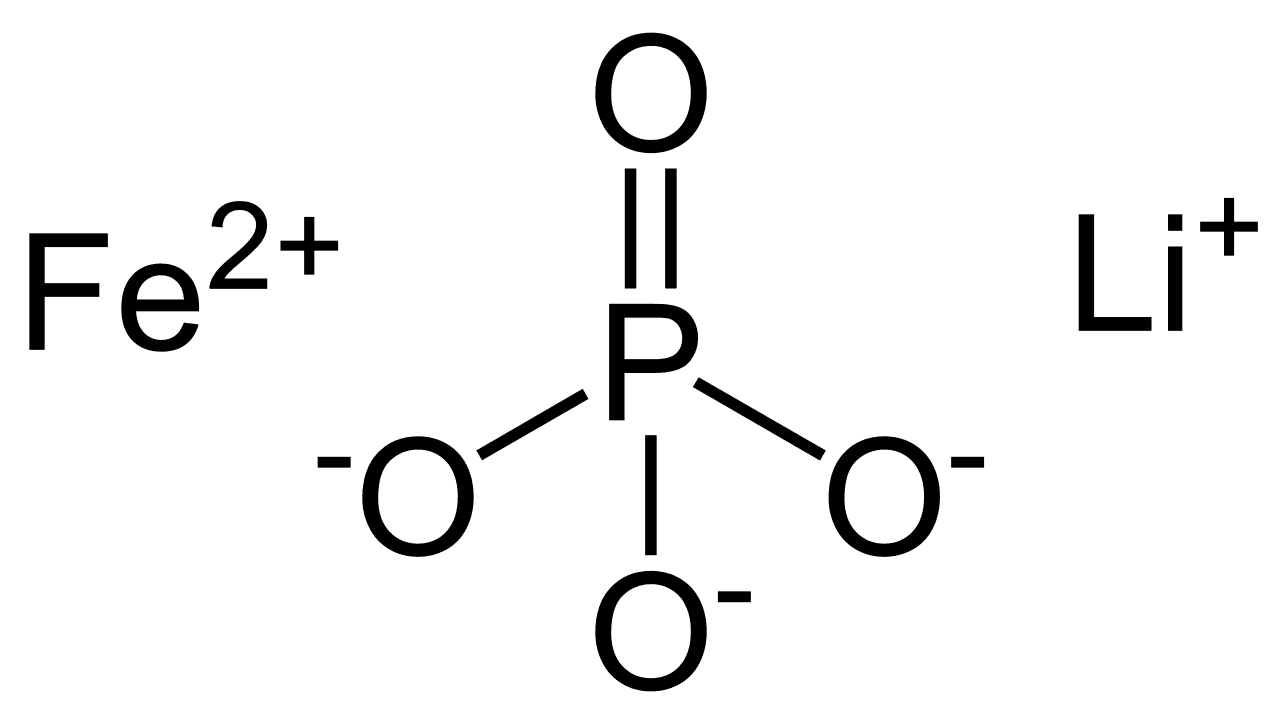
| Symbol | LiFePO4 |
| Color/Appearance | Metallic, Solid |
| Melting Point | >300 °C |
| Sputter | RF, RF-R, DC |
| Type of Bond | Indium, Elastomer |
| Available Sizes | Dia.: 1.0″, 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″, 6.0″ Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″ |
Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target Applications
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) sputtering targets are essential in several industries, particularly for the development of lithium-ion batteries and energy storage systems. These targets are vital for depositing thin films of LiFePO4 onto substrates, leveraging the material’s stability, high energy density, and safety. LiFePO4 is widely recognized as a preferred material in rechargeable battery technology.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target Bonding Services
Specialized bonding services for Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Targets, including indium and elastomeric bonding techniques, enhance performance and durability. Thin Film Materials (TFM) ensures high-quality solutions that meet industry standards and customer needs.
We also offer custom machining of backing plates, which is essential for sputtering target assembly. This comprehensive approach improves target design flexibility and performance in thin film deposition. Our channels provide detailed information about bonding materials, methods, and services, helping clients make informed decisions.

Lithium Iron Phosphate Sputtering Target Packing
Our Lithium Iron Phosphate sputter targets are tagged and labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. Great care is taken to avoid any damage that might be caused during storage or transportation.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.