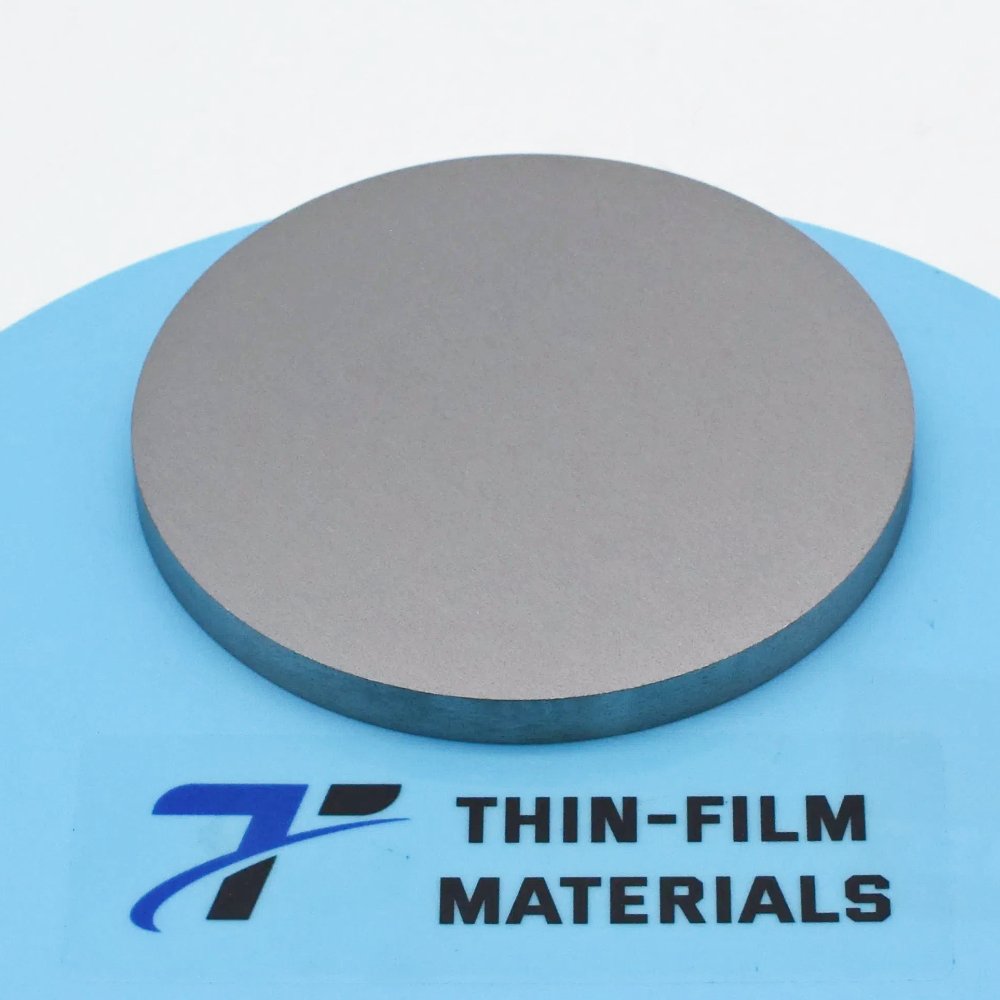
Tungsten Zirconium Boride (WZrB) Sputtering Target Description
Discover the exceptional performance of Tungsten Zirconium Boride (WZrB) Sputtering Targets, engineered for advanced thin-film deposition in cutting-edge industries. This page explores the superior qualities of WZrB alloys, offering unmatched durability and versatility for high-tech applications.
Tungsten: The Epitome of Strength
Tungsten (W), a refractory metal with the highest melting point of all elements (3,422°C), is renowned for its extreme hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Tungsten sputtering targets are critical for applications requiring robust coatings, such as semiconductor diffusion barriers, wear-resistant surfaces, and high-temperature electronics.
Zirconium Boride: Synergy of Lightweight and Toughness
Zirconium Boride (ZrB), a ceramic compound, combines the refractory properties of zirconium with the hardness of boron. It exhibits exceptional thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for aerospace, nuclear reactors, and ultra-high-temperature coatings.
Related Products: Tungsten Sputtering Target, Zirconium Boride Sputtering Target.
Tungsten Zirconium Boride Sputtering Target Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Tungsten Zirconium Boride (WZrB) |
| Chemical Symbol | W/Zr/B |
| Color/Appearance | Metallic gray, solid |
| Available Sizes | Dia.: 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″; Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″. Custom sizes available. |
| Purity | 99.7% (Standard), up to 99.999% on request. |
| Packing | Individually tagged, vacuum-sealed for quality control and safe shipping. |
WZrB Sputtering Target Applications
Wear-Resistant Coatings: Ideal for tools, molds, and mechanical components requiring extreme durability.
Semiconductor Barriers: Used in diffusion barriers for integrated circuits and microelectronics.
High-Temperature Films: Essential for aerospace and energy sectors due to thermal stability.
Advanced Optics: Enhances reflective coatings and optical communication devices.
WZrB Sputtering Target Advantages
✅ Unmatched Hardness: Combines tungsten’s strength with ZrB’s oxidation resistance.
✅ Thermal Stability: Performs reliably in extreme environments (up to 2,000°C).
✅ Customizable: Tailored purities, sizes, and shapes to meet specific deposition needs.
✅ Innovation-Driven: Enables breakthroughs in nanotechnology, renewable energy, and defense.
Unlock the Potential of WZrB Sputtering Targets
Elevate your thin-film technology with our high-performance Tungsten Zirconium Boride targets. Contact us today for customized solutions that push the boundaries of material science.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.