Niobium Sputtering Target Description
 Niobium sputtering targets retain the properties of their source material, niobium. This silver-colored metal is typically found alongside tantalum, with the two elements being separated through the fractional crystallization of their fluoro-complexes. Niobium is relatively abundant, comprising about 20 parts per million (ppm) of the Earth’s crust. As a pure metal, niobium is highly reactive and forms a very stable oxide layer when exposed to air, significantly enhancing its corrosion resistance. Additionally, niobium can react with various non-metals at elevated temperatures.
Niobium sputtering targets retain the properties of their source material, niobium. This silver-colored metal is typically found alongside tantalum, with the two elements being separated through the fractional crystallization of their fluoro-complexes. Niobium is relatively abundant, comprising about 20 parts per million (ppm) of the Earth’s crust. As a pure metal, niobium is highly reactive and forms a very stable oxide layer when exposed to air, significantly enhancing its corrosion resistance. Additionally, niobium can react with various non-metals at elevated temperatures.
Niobium Sputtering Target Specification
| Material Type | Niobium |
| Symbol | Nb |
| Atomic Number | 41 |
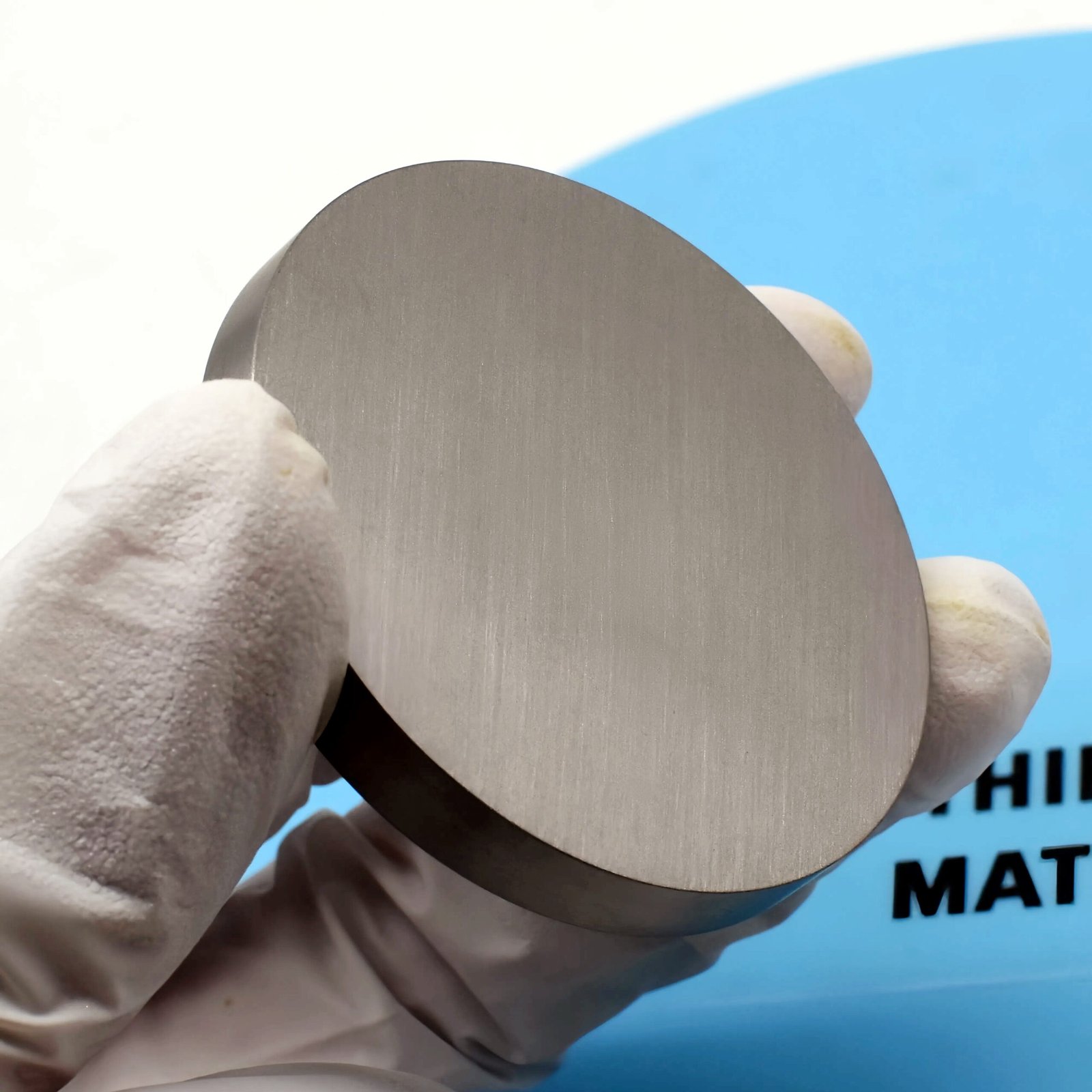
| Color/Appearance | Gray, Metallic |
| Melting Point | 2,468 °C |
| Density | 8.57 g/cc |
| Sputter | DC |
| Type of Bond | Indium, Elastomer |
| Comments | Attacks W source. |
| Target Dimensions & Thickness | Dia.: 1.0″, 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″, 6.0″ Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″ |
We also offer other customized shapes and sizes of the sputtering targets; please Contact Us for more information.
Niobium Sputtering Target Application
Niobium sputter targets are essential for thin film deposition in various applications, including fuel cells, decoration, semiconductors, displays, LEDs, photovoltaic devices, and glass coating. Beyond these uses, niobium has several other significant applications:
Steel Production Niobium is an effective microalloying element in steel, forming niobium carbide and niobium nitride. These compounds enhance grain refinement and slow down recrystallization and precipitation hardening processes. Niobium alloys are commonly used in pipeline construction due to these properties.
Superalloys Niobium is used in nickel-, cobalt-, and iron-based superalloys in quantities up to 6.5%. These superalloys are critical for jet engine components, gas turbines, rocket subassemblies, turbocharger systems, and heat-resistant combustion equipment. Niobium helps to precipitate a hardening γ”-phase within the grain structure of the superalloy, increasing its durability and performance.
Superconducting Magnets Niobium is used in the creation of type II superconductor wires, such as niobium-germanium (Nb3Ge), niobium-tin (Nb3Sn), and niobium-titanium alloys. These superconducting magnets are vital components in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) instruments, and particle accelerators.
Niobium Sputtering Target Bonding Services
Specialized bonding services for Niobium Sputtering Targets, including indium and elastomeric bonding techniques, enhance performance and durability. Thin Film Materials (TFM) ensures high-quality solutions that meet industry standards and customer needs.
We also offer custom machining of backing plates, which is essential for sputtering target assembly. This comprehensive approach improves target design flexibility and performance in thin film deposition. Our channels provide detailed information about bonding materials, methods, and services, helping clients make informed decisions.

Packing
Our Niobium Sputtering Targets are clearly tagged and labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. We take great care to prevent any damage during storage and transportation.
Get Contact
TFM offers Niobium Sputtering Targets in various forms, purities, sizes, and prices. We specialize in high-purity thin film deposition materials with optimal density and minimal grain sizes, which are ideal for semiconductor, CVD, and PVD applications in display and optics. Contact Us for current pricing on sputtering targets and other deposition materials that are not listed.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.