Overview of ConFlat Flanges
The CF (ConFlat) flange is the premier choice for high vacuum (HV) and ultra-high vacuum (UHV) applications, offering a reliable solution for a wide array of gauges, instruments, accessories, and feedthroughs. Its versatility and robustness make it essential in various vacuum systems.
Blank (Blind) Flanges
A blank, or blind flange, is a solid, disc-shaped fitting used in vacuum systems. This type of flange can be machined for a custom fit or to seal off unused sections of tubing or ports in vacuum chambers, ensuring effective containment.
Seal Mechanism
The CF flange’s sealing mechanism features a knife-edge that is precisely machined below the flat surface of the flange. When the bolts of a flange pair are tightened, these knife-edges create annular grooves on either side of a soft metal gasket. The extruded metal effectively fills any machining marks and surface imperfections, resulting in a leak-tight seal. The CF seal operates efficiently across a pressure range from 760 torr (103 mbar) to less than 1 x 10^-13 Torr (approximately 1.3 x 10^-13 mbar), and it functions within a temperature range of -196°C to 450°C, depending on the materials used.
In North America, flange sizes are typically referenced by their outside diameter (O.D.), while in Europe and much of Asia, the nominal internal diameter (I.D.) of the largest tube that can be welded to a bored flange is usually used for identification.
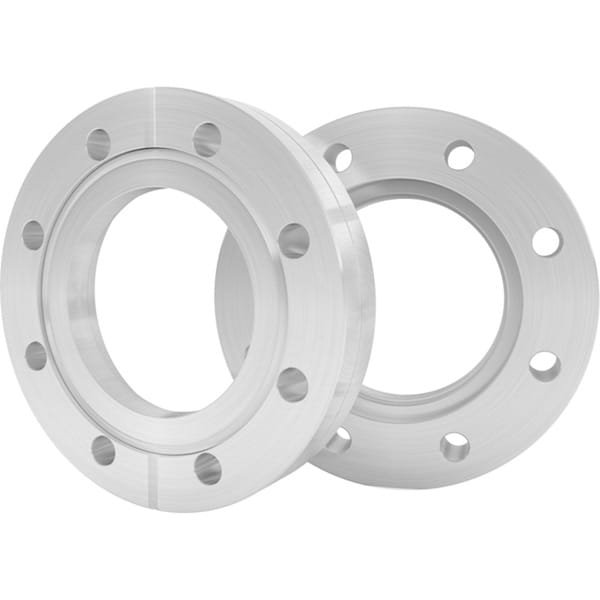
Types of ConFlat Flanges
ConFlat flanges come in four main configurations:
- Fixed Flange: This one-piece design has a fixed bolt-hole orientation relative to the fitting, ensuring stable alignment during assembly.
- Rotatable Flange: Comprised of an inner weld ring and an outer bolt ring, this configuration allows the bolt ring to rotate around the inner weld ring, providing flexibility for alignment adjustments.
Both fixed and rotatable flanges are available with options for through (clearance) holes or tapped holes, allowing for customization to meet specific application needs.
Through (Clearance) Holes

Are through-holes that allow adequate clearance for bolts to go through both flanges and secured by nuts or plate nuts.
Tapped Holes

Are imperial or metric threaded holes machined through the flange. This allows a clearance-hole flange to be connected without the need for nuts or plate nuts. Be aware of a components bolt hole orientation when selecting tapped flanges.
Ordering Table
| Flange Size/OD | Type | Note | Part Number |
| DN16CF (1.33" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0133X025R |
| DN16CF (1.33" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0133X037R |
| DN16CF (1.33" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0133X050R |
| DN16CF (1.33" OD) | Rotatable | 1 | F0133X075R |
| DN16CF (1.33" OD) | Rotatable Weldneck | — | F0133X075RW |
| DN25CF (2.13" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0212X025R |
| DN25CF (2.13" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0212X050R |
| DN25CF (2.13" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0212X075R |
| DN25CF (2.13" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0212X100R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X025R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X050R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X075R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X100R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X125R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X150R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X162R |
| DN35CF-DN40CF (2.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0275X175R |
| DN50CF (3.38" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0337X150R |
| DN50CF (3.38" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0337X200R |
| DN63CF (4.50" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0450X150R |
| DN63CF (4.50" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0450X200R |
| DN63CF (4.50" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0450X250R |
| DN75CF (4.63" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0462X250R |
| DN75CF (4.63" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0462X300R |
| DN100CF (6.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0600X400R |
| DN125CF (6.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0675X400R |
| DN125CF (6.75" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0675X500R |
| DN160CF (8.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0800X600R |
| DN160CF (8.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F0800X608R |
| DN200CF (10.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F1000X800R |
| DN250CF (12.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F1200X1000R |
| DN275CF (13.25" OD) | Rotatable | — | F1325X1000R |
| DN275CF (13.25" OD) | Rotatable | F1325X1075R | |
| DN295CF (14.00" OD) | Rotatable | — | F1400X1200R |
| DN350CF (16.50" OD) | Rotatable | — | F1650X1400R |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.